Mechanism Of Blood Coagulation Chart Blood Coagulation Pathway The process of blood coagulation leads to haemostasis i e prevention of bleeding or haemorrhage Blood clotting involves activation and aggregation of platelets at the exposed endothelial cells followed by
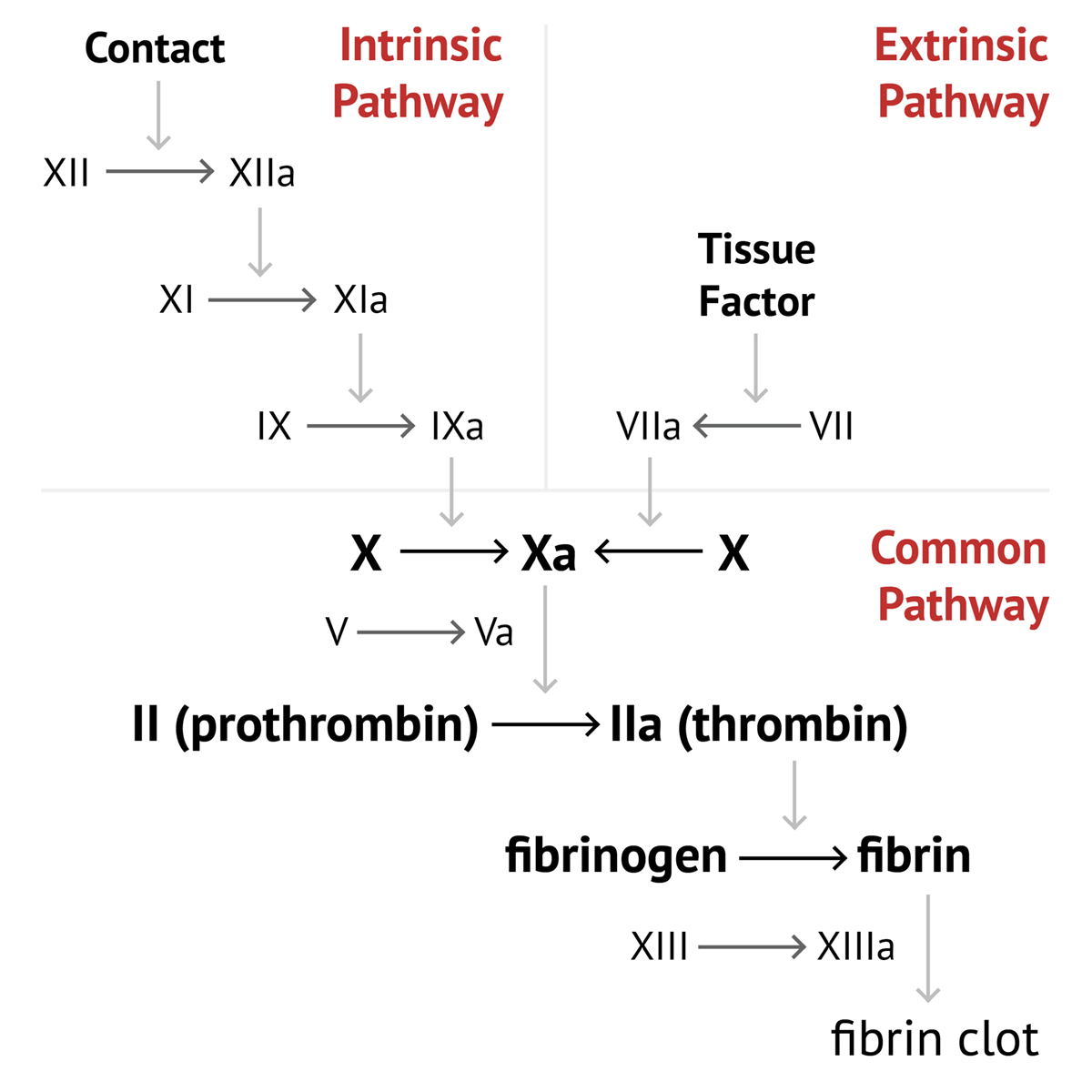
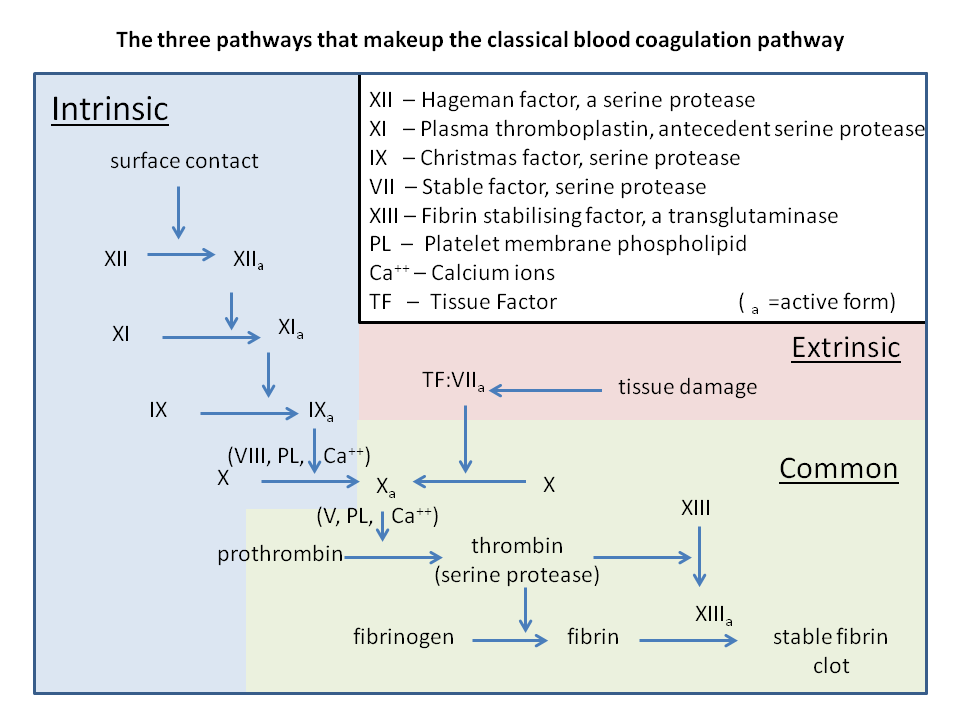
Mechanism The mechanism by which coagulation allows for hemostasis is an intricate process that is done through a series of clotting factors The intrinsic pathway consists of factors I II IX X XI and XII Respectively each one is named fibrinogen prothrombin Christmas factor Stuart Prower factor plasma thromboplastin and Coagulation also known as clotting is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel forming a blood clot It results in hemostasis the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel followed by repair The process of coagulation involves activation adhesion and aggregation of platelets as well as deposition and
Mechanism Of Blood Coagulation Chart
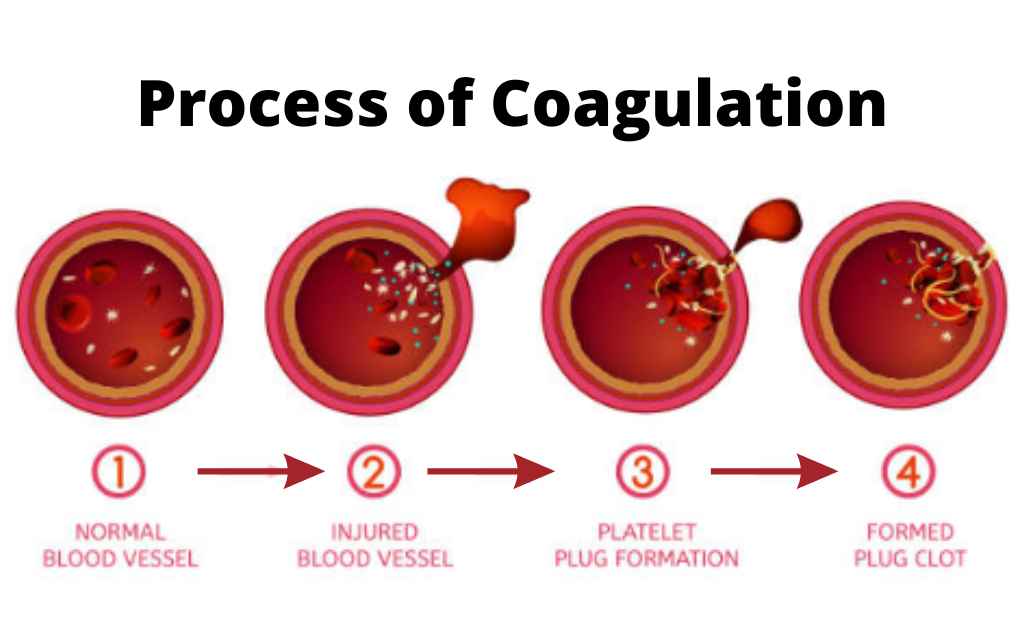
Mechanism Of Blood Coagulation Chart
https://eduinput.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Process-of-Coagulation_11zon.jpg

Hemostasis And Blood Coagulation Blood Coagulation Tests
https://alpha.uscreencdn.com/assets/621/player_image/1869900/220909-FC-06-Blood-Coagulation-Tests-PLAYER.1663257984.jpg
Coagulation Part 7 Blood Coagulation Factors Descriptions Labpedia
https://www.labpedia.net/wp-content/uploads/-coagulation-part-7-blood-coagulation-factors-descriptions-/coagulation-pathways-23.JPG
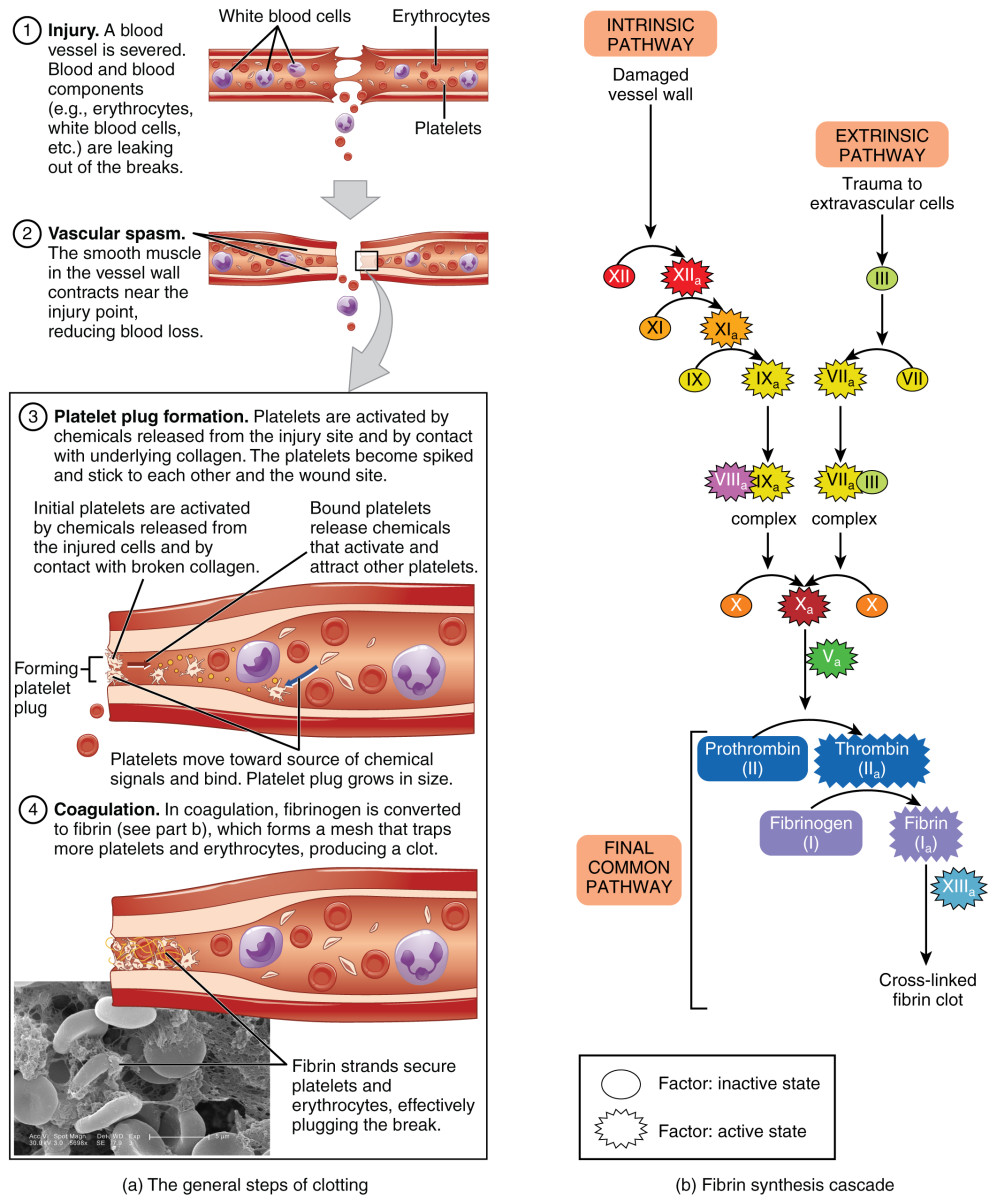
Pink border represents intrinsic pathway green border represents extrinsic pathway and orange border represents final common pathway of blood coagulation Proteins involved in the main pathway are colored in blue whereas regulatory proteins are Vascular mechanisms platelets coagulation factors prostaglandins enzymes and proteins are the contributors to the clotting mechanism which act together to form clots and stop a loss of blood Through vasoconstriction adhesion activation and aggregation the contributors form a transient plug to act as the cork to the leaking blood flow
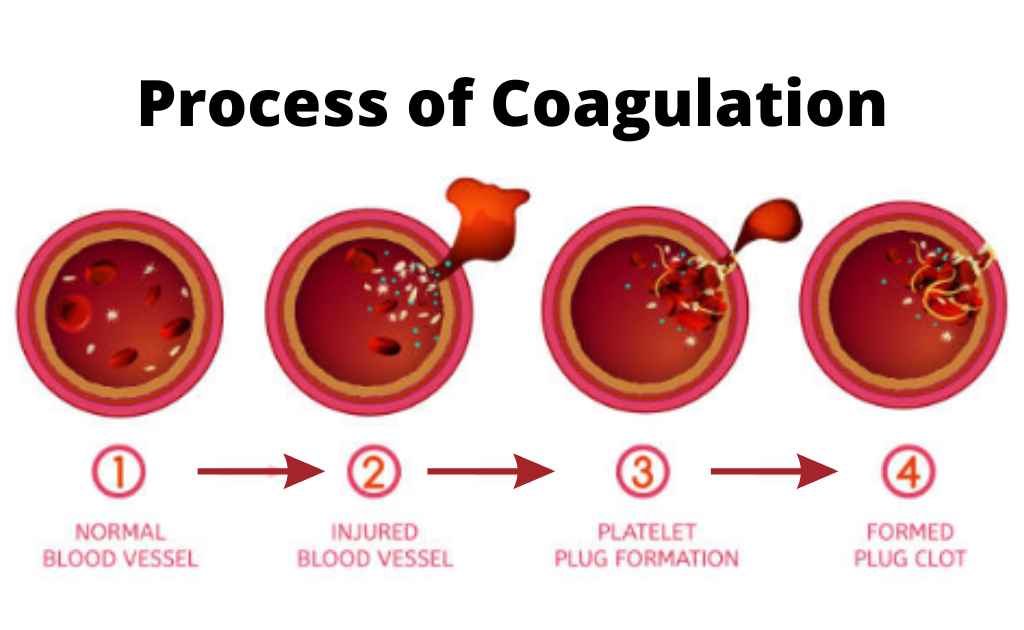
Blood clotting or coagulation can reduce the supply of nutrients and oxygen to blood vessels The coagulation happens through a cascade process in which the protease enzyme thrombin plays Clotting of blood Coagulation or blood clotting is a physiological process in our bodies It prevents excessive bleeding Platelets and clotting factors work together to seal the site of the injury The clot will dissolve after the damage heals Steps in the blood clotting process The clotting process occurs in multiple steps
More picture related to Mechanism Of Blood Coagulation Chart
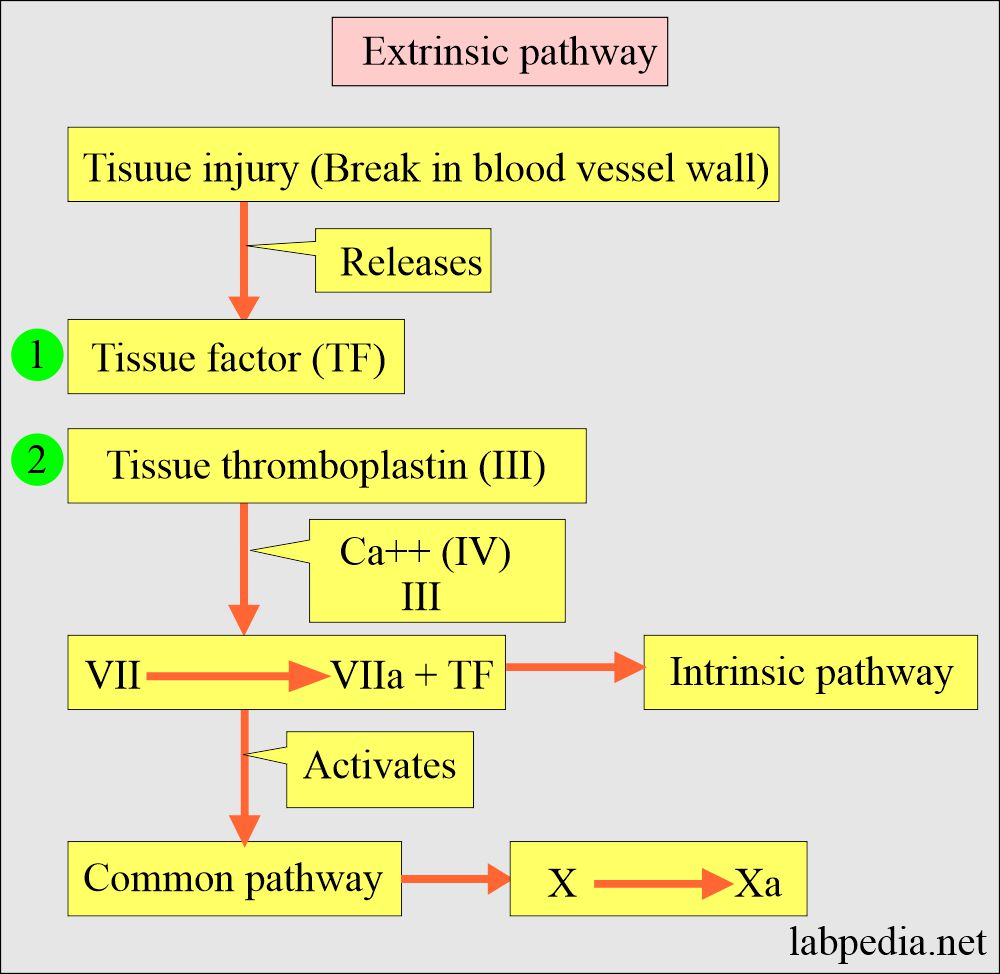
Coagulation Part 1 Blood Coagulation Process Coagulation Factors And Factors Deficiency
https://labpedia.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Extrinsic-pathway-cycle-1.jpg

816 Blood Coagulation Patient Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
https://www.shutterstock.com/shutterstock/photos/2097149680/display_1500/stock-photo-blood-sample-for-activated-partial-thromboplastin-time-aptt-test-blood-coagulation-testing-2097149680.jpg
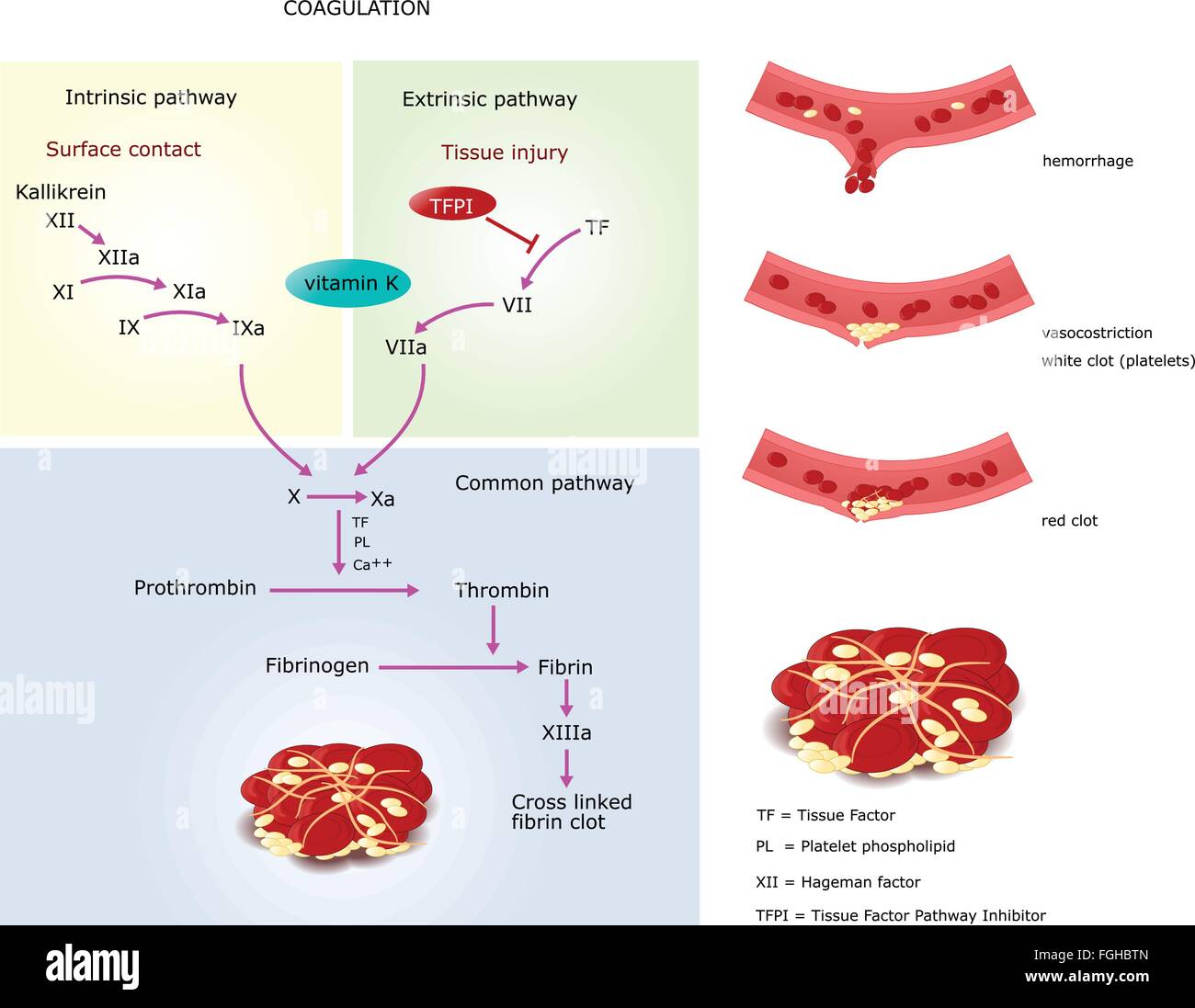
Mechanism Of Coagulation In Human Blood Via Intrinsic And Extrinsic Stock Vector Art
http://c8.alamy.com/comp/FGHBTN/mechanism-of-coagulation-in-human-blood-via-intrinsic-and-extrinsic-FGHBTN.jpg
Coagulation is initiated when tissue factor TF normally segre gated from the flowing blood is exposed to plasma binding co agulation factor F VII VIIa and forming a complex on cellular surfaces that triggers the coagulation cascade The mechanism of hemostasis can divide into four stages 1 Constriction of the blood vessel 2 Formation of a temporary platelet plug 3 Activation of the coagulation cascade 4 Formation of fibrin plug or the final clot
The document summarizes the process of blood coagulation It discusses that coagulation occurs through a series of reactions activating clotting factors which convert fibrinogen into fibrin forming a mesh that traps blood cells Blood coagulation refers to the process of forming a clot to stop bleeding Coagulation is a complicated subject and is greatly simplified here for the student s understanding Primary hemostasis involves the first two processes 1 Vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction is the body s first response to injury in the vascular wall
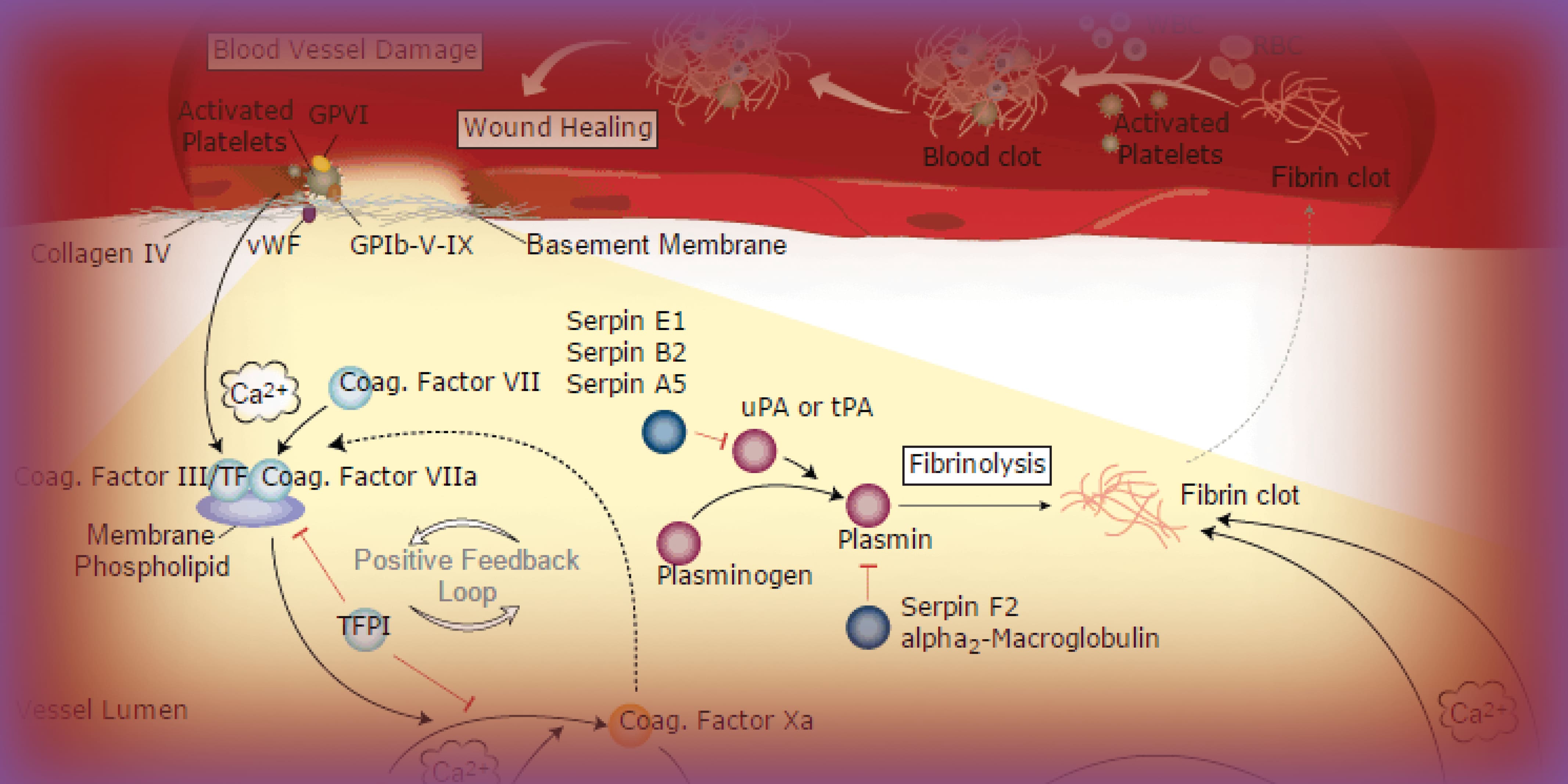
Blood Coagulation Pathway And Resources
https://resources.rndsystems.com/images/blog/blood-coag-blog-header.jpg

Blood Coagulation Blood Clotting
http://www.clotbase.bicnirrh.res.in/img/path2.jpg
https://byjus.com › neet › mechanism-of-blood-coagulation-notes
Blood Coagulation Pathway The process of blood coagulation leads to haemostasis i e prevention of bleeding or haemorrhage Blood clotting involves activation and aggregation of platelets at the exposed endothelial cells followed by

https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov › books
Mechanism The mechanism by which coagulation allows for hemostasis is an intricate process that is done through a series of clotting factors The intrinsic pathway consists of factors I II IX X XI and XII Respectively each one is named fibrinogen prothrombin Christmas factor Stuart Prower factor plasma thromboplastin and

Coagulation Cascade What Is It Steps And More Osmosis

Blood Coagulation Pathway And Resources

Extrinsic Coagulation Pathway
Coagulation Factors
How Blood Clots Platelets And The Coagulation Cascade Owlcation

Biochemistry How Does Alum Help In Blood Coagulation Biology Stack Exchange

Biochemistry How Does Alum Help In Blood Coagulation Biology Stack Exchange
Coagulation Profile
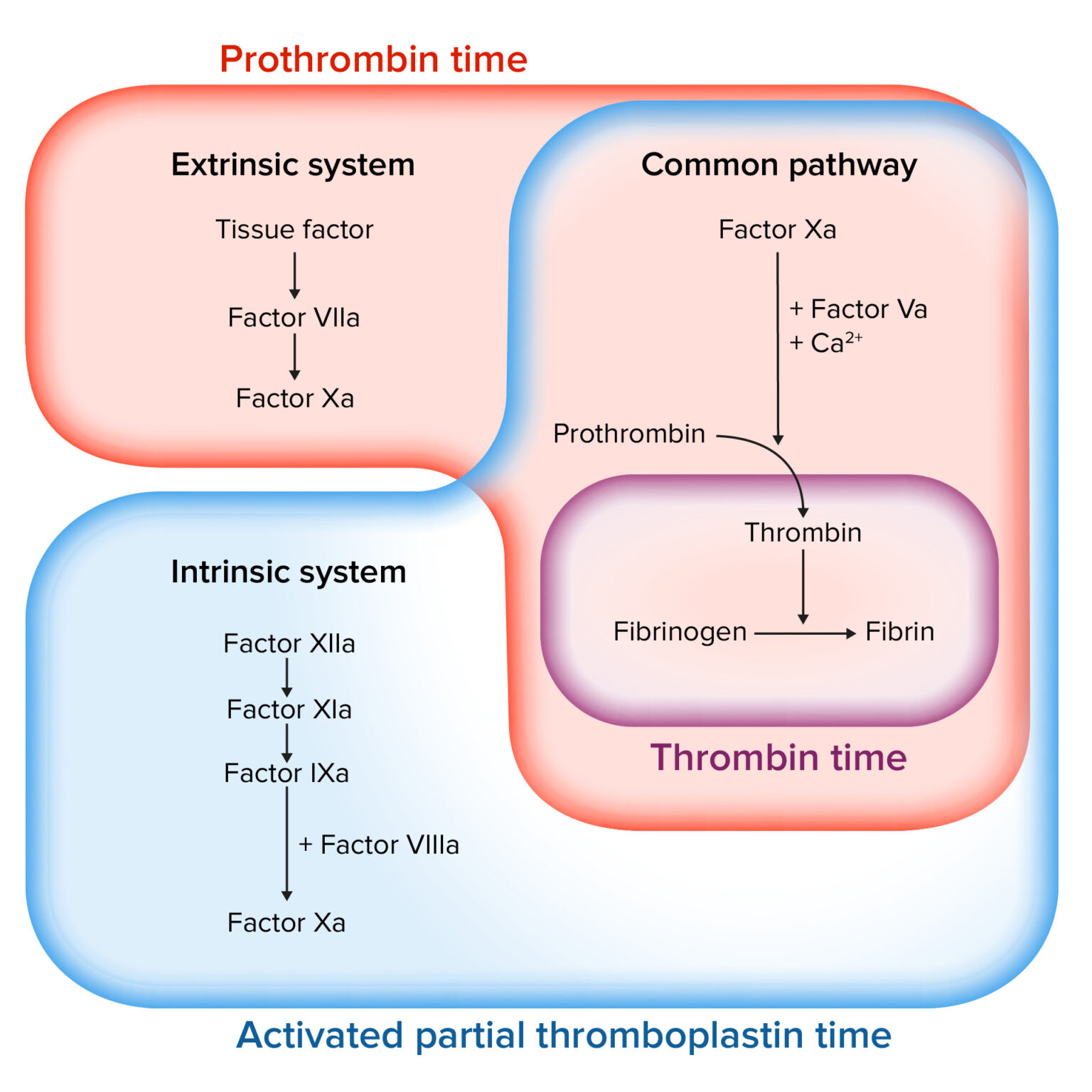
Coagulation Studies Concise Medical Knowledge

Positive Feedback Mechanism Blood Clotting
Mechanism Of Blood Coagulation Chart - Clotting of blood Coagulation or blood clotting is a physiological process in our bodies It prevents excessive bleeding Platelets and clotting factors work together to seal the site of the injury The clot will dissolve after the damage heals Steps in the blood clotting process The clotting process occurs in multiple steps