Chart Blood Transfusion Guidelines Sickle Cell We highlight the roles of RBC transfusions in preventing or mitigating neurological disease in reducing perioperative complications in managing acute chest syndrome and in optimizing pregnancy outcomes in SCD We further highlight various transfusion techniques and when each might be considered
Sickle Cell Disease is lifelong and can be life limiting The condition is characterised by anaemia episodes of acute painful crisis and an increased risk of infection Clinical presentation and severity can be wide ranging Authorised personnel specific staff competencies For children with HbSS or HbS 0 thalassemia and a history of prior ischemic stroke the ASH guideline panel recommends blood transfusion goals for secondary stroke prevention of increasing the hemoglobin above 9 g dL at all times and maintaining the HbS level at
Chart Blood Transfusion Guidelines Sickle Cell

Chart Blood Transfusion Guidelines Sickle Cell
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351168977/figure/fig1/AS:11431281184453177@1693337835355/Adherence-to-guidelines-of-blood-transfusion-in-patients-with-sickle-cell-disease.png

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell
https://www.omicsonline.org/articles-images/blood-disorders-transfusion-KFH-hospital-guidelines-8-381-g001.png

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell
https://www.aafp.org/content/dam/brand/aafp/pubs/afp/issues/2015/1215/p1069-t4.gif
Guidance for specific indications and administration of transfusion as well as screening prevention and management of alloimmunization delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions DHTRs and iron overload may improve outcomes The red cell units selected for transfusion should be ABO compatible Rh and Kell matched HbS negative and antigen negative for any clinically significant red cell antibodies Where possible blood for top up transfusion should be
Exchange transfusion is a potentially lifesaving procedure that allows correction of anaemia without increasing blood viscosity and may improve tissue oxygenation whilst reducing microvascular sickling The aim of exchange transfusion is to lower the HbS level to 30 or less while keeping the Haemoglobin close to 100g l Transfusion in SCD requires careful consideration of both the haemoglobin concentration Hb and or percentage of sickle haemoglobin HbS in order to ensure maximal oxygen delivery to tissues without increasing overall blood viscosity to detrimental levels Grade 1C
More picture related to Chart Blood Transfusion Guidelines Sickle Cell

American Society Of Hematology Sickle Cell Patient Care Guidelines Sickle Cell
https://sickle-cell.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/[email protected]

Exchange Transfusion In Sickle Cell Disease ScienceHUB
https://i2.wp.com/www.thelancet.com/cms/attachment/2100904531/2079768691/gr2_lrg.jpg

PDF Red Blood Cell Transfusion In Sickle Cell Disease
https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/371494231_Red_blood_cell_transfusion_in_sickle_cell_disease/links/64870dced702370600ef2231/largepreview.png
Transfusion should ideally be given only after discussion with the haematology service SCD patients needing transfusion must be given ABO Rh CcDEe and Kell compatible units Blood should be antigen negative for clinically significant antibodies that are currently or have previously been detected Blood bank must be Guidance for specific indications and administration of transfusion as well as screening prevention and management of alloimmunization delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions DHTRs and iron overload may improve outcomes
The objective of the Best Practices in Transfusion Medicine for Patients with Sickle Cell Disease SCD Conference was to review the available published evidence and clinical experience surrounding the use of RBC transfusions for sickle cell disease by a panel of experts To minimize adverse effects of transfusion the selection and infusion of erythrocyte units should follow standard blood banking and transfusion practices
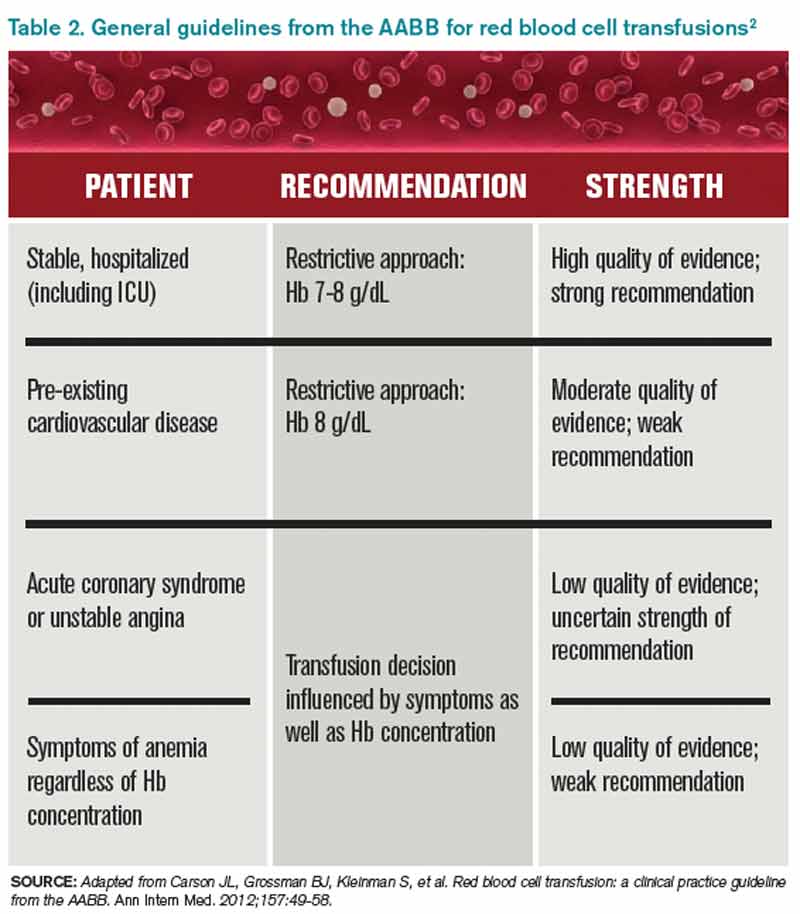
Blood Transfusion Chart
https://cdn.mdedge.com/files/s3fs-public/images/TH_2013_09_pp22_T01_LG.jpg
Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell
https://www.the-hospitalist.org/wp-content/uploads/legacy/files/122854_table_2_web.JPG

https://ashpublications.org › hematology › article › ...
We highlight the roles of RBC transfusions in preventing or mitigating neurological disease in reducing perioperative complications in managing acute chest syndrome and in optimizing pregnancy outcomes in SCD We further highlight various transfusion techniques and when each might be considered
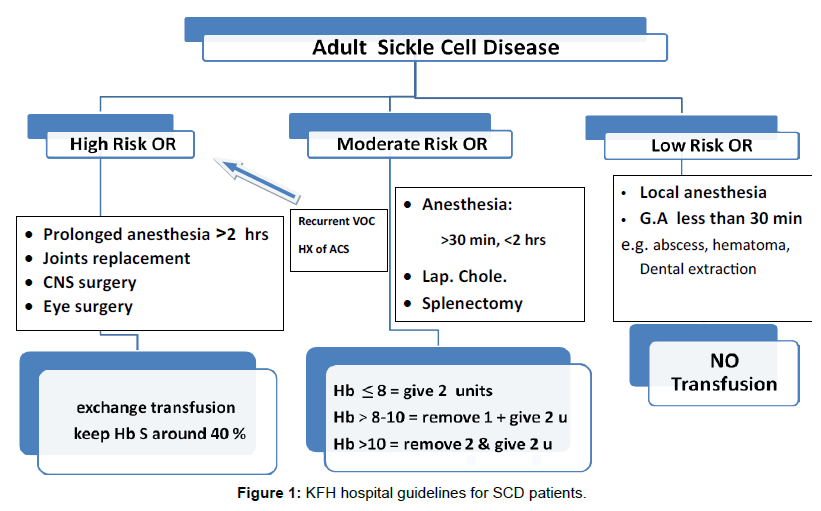
https://clinicalguidelines.scot.nhs.uk › ... › sickle-cell-protocol
Sickle Cell Disease is lifelong and can be life limiting The condition is characterised by anaemia episodes of acute painful crisis and an increased risk of infection Clinical presentation and severity can be wide ranging Authorised personnel specific staff competencies
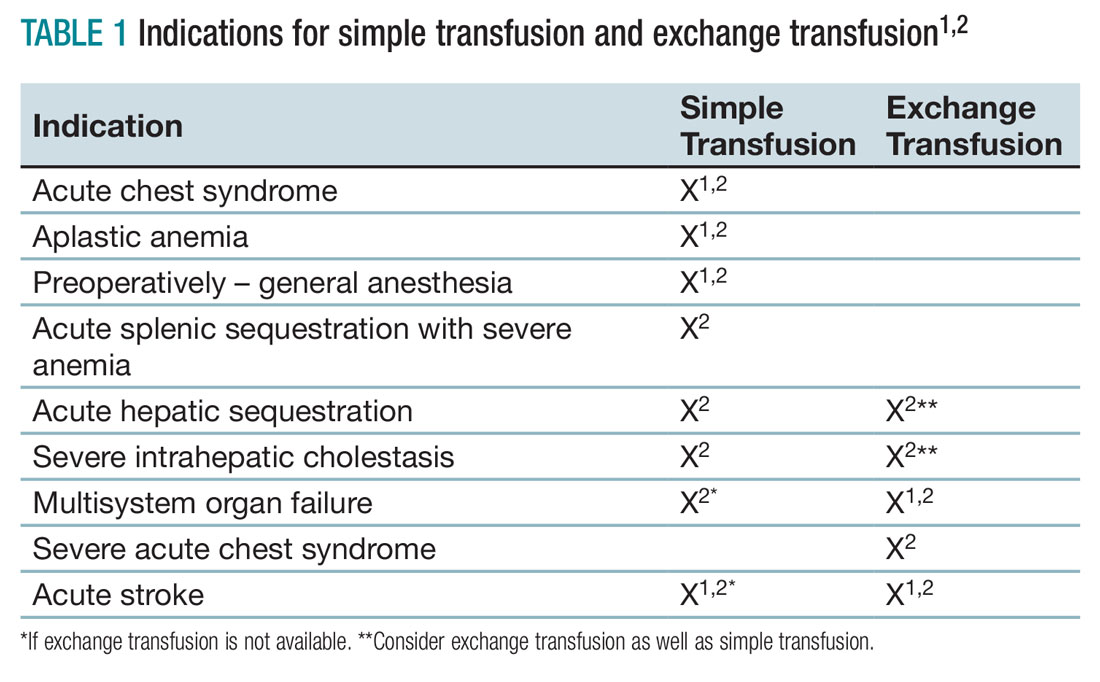
Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell

Blood Transfusion Chart

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell
.jpg)
Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell
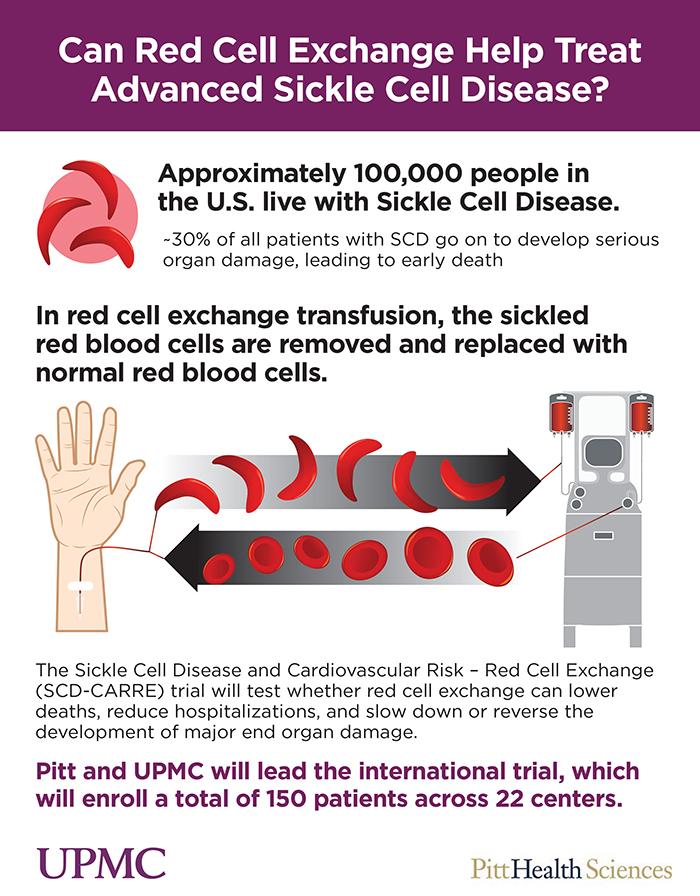
Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell

Exchange Transfusion Sickle Cell

Sickle Cell Patient Has Blood Transfusion In Arm Stock Image M532 0486 Science Photo Library
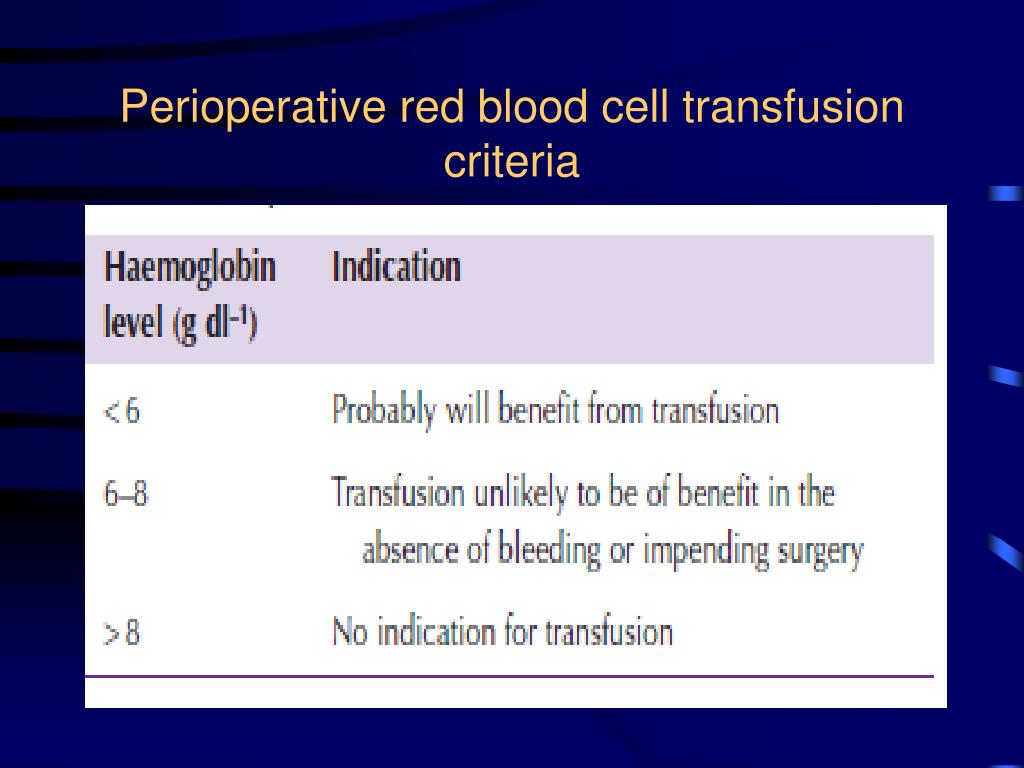
Red Blood Cell Transfusion
Chart Blood Transfusion Guidelines Sickle Cell - Exchange transfusion is a potentially lifesaving procedure that allows correction of anaemia without increasing blood viscosity and may improve tissue oxygenation whilst reducing microvascular sickling The aim of exchange transfusion is to lower the HbS level to 30 or less while keeping the Haemoglobin close to 100g l