Blood Lead Level Chart Treatment Identification and removal from lead exposure is the primary treatment of elevated BLL and most cases of symptomatic lead toxicity Chelation therapy is reserved for patients with severe symptoms of toxicity which typically occur at BLL greater than 80 g dL or in any patient with an extremely high BLL e g 100 g dL
CDC recommends testing blood for lead exposure Two types of blood collection tests may be used A patient s blood lead level BLL is measured in micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood g dL Recommendations are provided for initial screening capillary and Blood lead level BLL monitoring should be done on a schedule based on an individual s risk of exposure to lead Primary management of lead poisoning is source identification and the elimination or reduction of further exposure
Blood Lead Level Chart Treatment

Blood Lead Level Chart Treatment
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Annika-Dean-2/publication/321799012/figure/tbl3/AS:613857408081938@1523366419691/Blood-lead-level-results.png

Blood Lead Testing
https://www.michigan.gov/mileadsafe/-/media/Project/Websites/mileadsafe/Photos/Lead-Level-Adobe.jpeg?rev=ab9fe7508c5f4c3da47e52a9c53835e0&hash=1FAC8B85AD7C4AAB1D906BDEEB6AEDF0
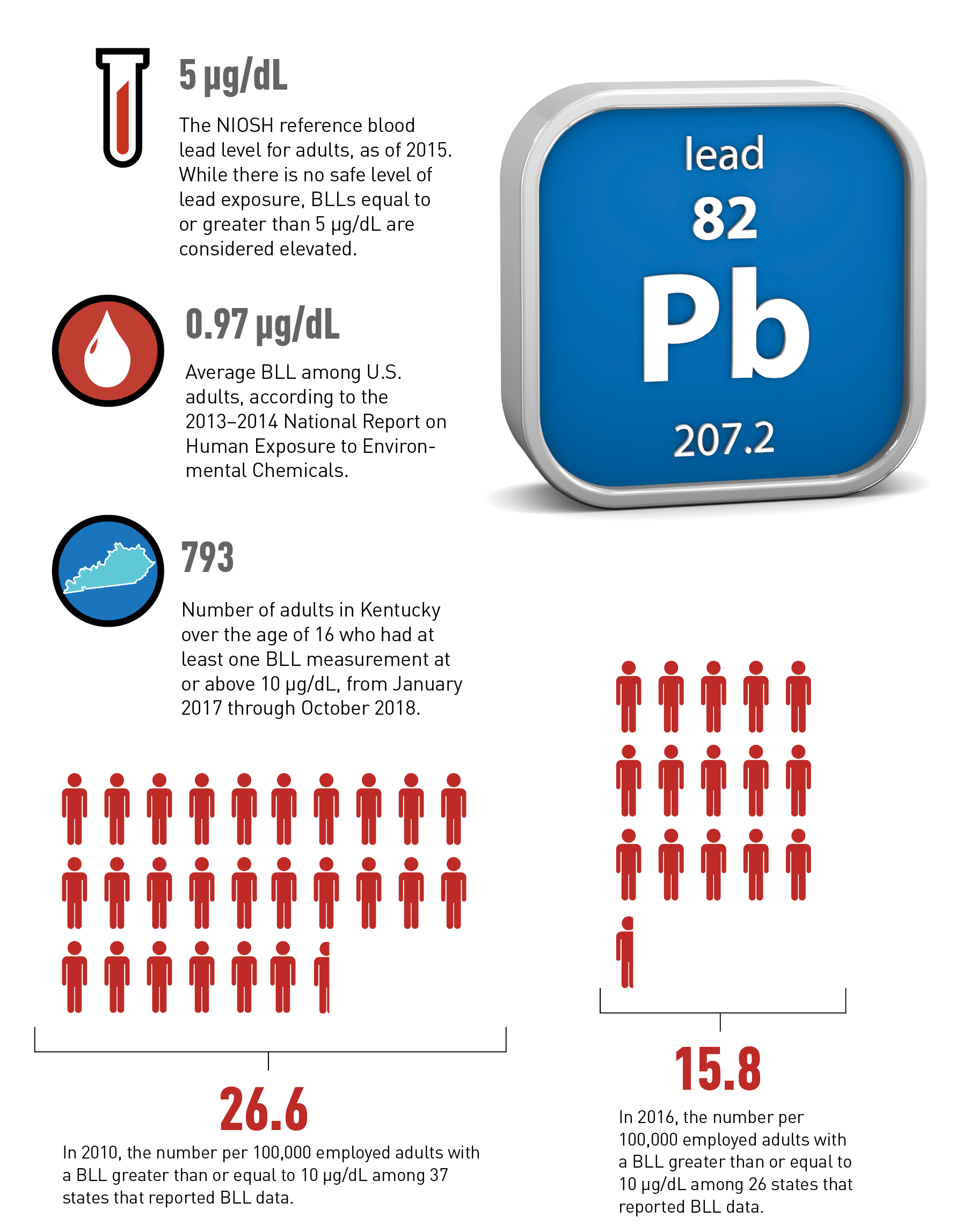
Blood Lead Levels In Kentucky Workers
https://synergist.aiha.org/image/5350856.1584548077000/img_202004-BTN.png
Healthcare providers will decide on the best treatment based on the level of lead in the blood The Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA and a few state agencies regulate BLLs in workers Other government agencies and non government groups offer recommended lead exposure limits s health consequences if not diagnosed early Case management focuses on reducing exposure to lead and decreasing the patient s Blood Lead Level BLL whethe symptoms of lead toxicity are present or not Table 1 and 2 discuss the recommended ac
This resource is an evidence based guide on follow up care for children based on blood lead levels measured in g dL micrograms per deciliter It details steps for care management based on the following categories of blood lead level For a non pregnant adolescent or adult with a blood lead concentration 70 100 g dL and with significant neurological features of lead toxicity e g irritability drowsiness ataxia convulsions coma or lead encephalopathy urgent parenteral chelation therapy is recommended
More picture related to Blood Lead Level Chart Treatment

Elevated Blood Lead Investigations
https://www.tri-techtesting.com/publishImages/Elevated-Blood-Lead-Investigations~~element63.jpg

Estimated Distribution Of Blood Lead Level In Occupational Exposure To Download Scientific
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334198717/figure/fig2/AS:776587804942336@1562164369416/Estimated-distribution-of-blood-lead-level-in-occupational-exposure-to-lead.jpg

Comparison Of Mean Blood Lead Level With Different Groups Of Medical Download Scientific
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Soqrat-Omari-Shekaftik/publication/334593087/figure/tbl1/AS:895461254782982@1590506008634/Comparison-of-mean-blood-lead-level-with-different-groups-of-medical-records-variables_Q640.jpg
Those methods are 1 capillary finger stick which allows a large number of children to be screened and 2 venous draw blood taken from the vein and is very accurate The following chart informs you as to what to do when results are received from either method Recommended medical surveillance for all lead exposed workers should include quarterly blood lead measurements for individuals with blood lead concentrations between 10 and 19 g dL and semiannual blood lead measurements when sustained blood lead concentrations are 10 g dL
When blood lead concentrations are high and or the patient is showing significant features of lead toxicity chelation therapy to facilitate lead excretion may improve health outcomes as described in section 7 3 The purpose of the WHO Guideline for clinical management of exposure to lead is to assist physicians in making decisions about the diagnosis and treatment of lead exposure for individual patients and in mass poisoning incidents The guideline presents evidence informed recommendations on 1 2 3 4 use of nutritional supplements 01

Lead Poisoning INITIATIVE FOR COORDINATED
https://www.rama.mahidol.ac.th/icaps/sites/default/files/public/di 1_1.png

Lead Levels Blood
https://www.ucsfhealth.org/-/media/project/ucsf/ucsf-health/medical-tests/hero/lead-levels-blood-2x.jpg?h=1112&w=2880&hash=2802752A38A394CE950C4AE4BF0C51F5

https://www.cdph.ca.gov › ABLGuidelines
Identification and removal from lead exposure is the primary treatment of elevated BLL and most cases of symptomatic lead toxicity Chelation therapy is reserved for patients with severe symptoms of toxicity which typically occur at BLL greater than 80 g dL or in any patient with an extremely high BLL e g 100 g dL

https://stacks.cdc.gov › view › cdc
CDC recommends testing blood for lead exposure Two types of blood collection tests may be used A patient s blood lead level BLL is measured in micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood g dL Recommendations are provided for initial screening capillary and

Figure 1 From Blood Lead Level And Handgrip Strength In Preadolescent Polish Schoolchildren

Lead Poisoning INITIATIVE FOR COORDINATED

Geometric Blood Lead Levels According At Risk Activities Of Lead Download Scientific Diagram

Lead Levels Before And After Intervention In Children With Elevated Download Scientific Diagram

Table 1 From Blood Lead Level As Marker Of Increased Risk Of Ovarian Cancer In BRCA1 Carriers
+PDF+Image.jpg?MOD=AJPERES)
Prevalence Of Confirmed Elevated Blood Lead Levels Among Tested Ohio Children
+PDF+Image.jpg?MOD=AJPERES)
Prevalence Of Confirmed Elevated Blood Lead Levels Among Tested Ohio Children

Table 3 From Blood Lead Level As Marker Of Increased Risk Of Ovarian Cancer In BRCA1 Carriers

Table 2 From Blood Lead Level As Marker Of Increased Risk Of Ovarian Cancer In BRCA1 Carriers

Lead Levels Blood
Blood Lead Level Chart Treatment - For a non pregnant adolescent or adult with a blood lead concentration 70 100 g dL and with significant neurological features of lead toxicity e g irritability drowsiness ataxia convulsions coma or lead encephalopathy urgent parenteral chelation therapy is recommended