Blood Flow Chart Arteriole Capillary Hydrostatic Arterioles are the dominant site of resistance to blood flow within the organ Capillaries are the site of exchange Balance between hydrostatic and oncotic forces determines the direction of fluid movement either into or out of the capillaries Veins are the low resistance conduits for venous return and volume reservoirs 6
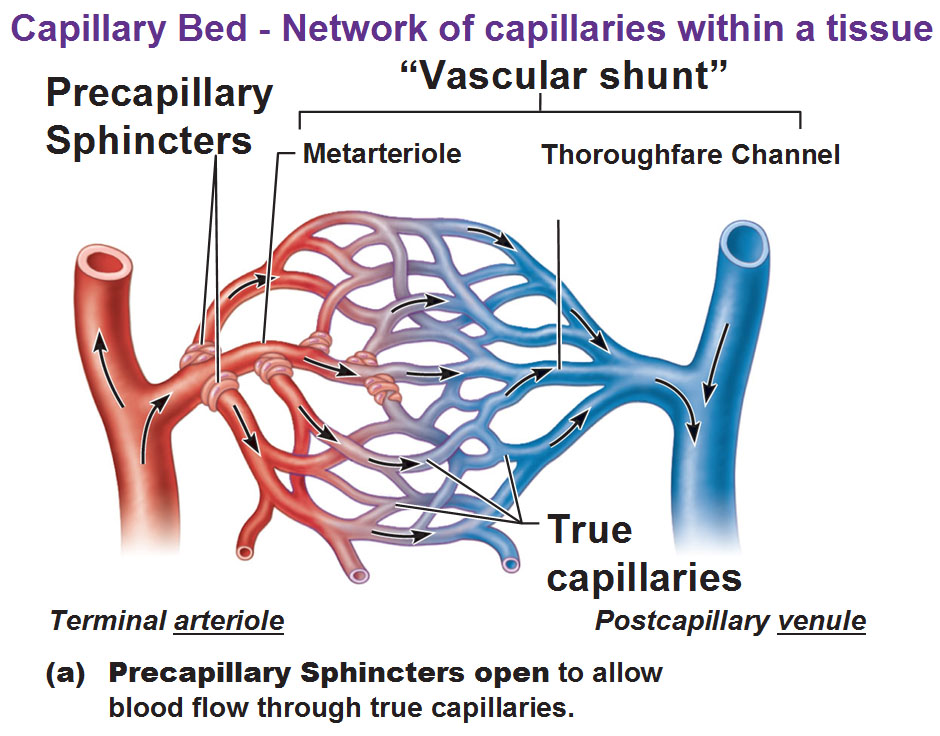
If the sphincters are open the blood will flow into the associated branches of the capillary blood If all of the sphincters are closed then the blood will flow directly from the arteriole to the venule through the thoroughfare channel see Figure 7 17 If the sphincters are open the blood will flow into the associated branches of the capillary blood If all of the sphincters are closed then the blood will flow directly from the arteriole to the venule through the thoroughfare channel see Figure 21 17
Blood Flow Chart Arteriole Capillary Hydrostatic

Blood Flow Chart Arteriole Capillary Hydrostatic
https://i0.wp.com/slideplayer.com/10475115/35/images/7/Hydrostatic+and+Oncotic+Pressure.jpg

Hydrostatic Pressure Capillary Blood Vessel Stock Illustration 1639917898 Shutterstock
https://image.shutterstock.com/shutterstock/photos/1639917898/display_1500/stock-photo-hydrostatic-pressure-in-capillary-or-blood-vessel-1639917898.jpg
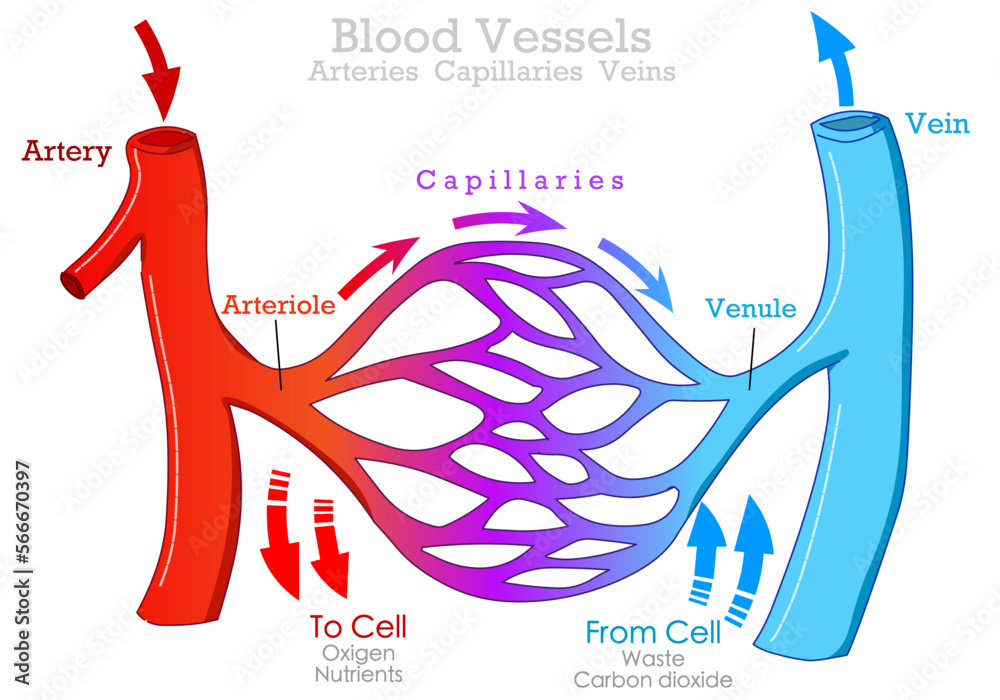
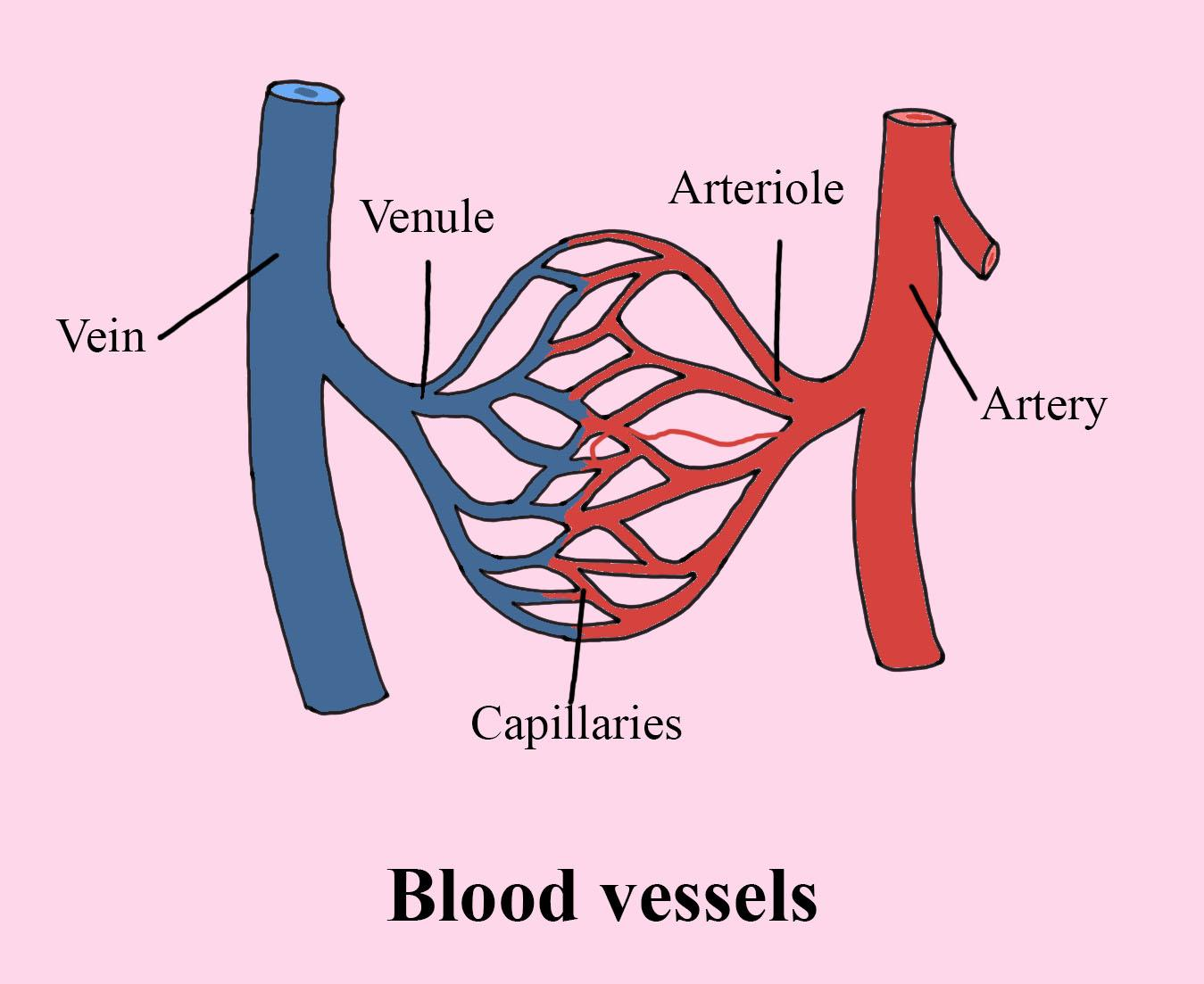
Blood Vessels Types Arteries Veins Capillaries Arteriole Venule Artery Carry Transport
https://as2.ftcdn.net/v2/jpg/05/66/67/03/1000_F_566670397_YPNN6BhK5lbewRRC1RDyZmEbLAfs6b8Q.jpg
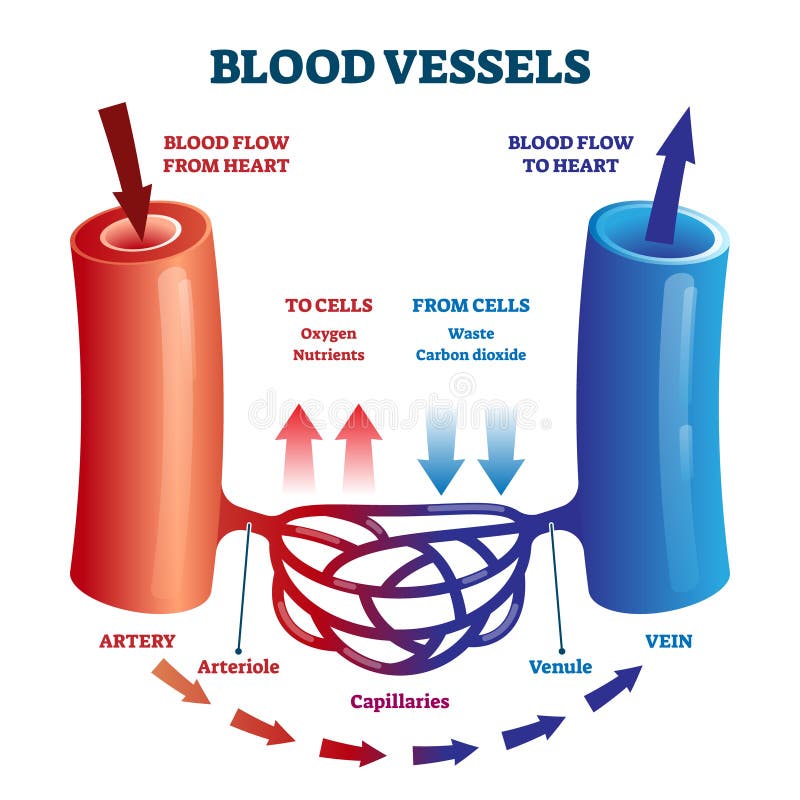
As blood is pumped away from the heart it travels through the aorta to arteries aterioles and the capillary beds Blood flow through the capillary beds reaches almost every cell in the body and is controlled to divert blood according to the body s needs Once gas exchange is completed oxygenated blood flows from the pulmonary capillaries into a series of pulmonary venules that eventually lead to a series of larger pulmonary veins Four pulmonary veins two on the left and two on the right return blood to the left atrium At this point the pulmonary circuit is complete
Blood hydrostatic pressure is the force exerted by the blood confined within blood vessels or heart chambers Even more specifically the pressure exerted by blood against the wall of a capillary is called capillary hydrostatic pressure CHP and is the same as capillary blood pressure On the arteriole side of the capillary the hydrostatic pressure i e the blood pressure is about 35 mm Hg pushing water and other small molecules out The blood osmotic pressure is 25 mm Hg pushing water and other small molecules in The net pressure 35
More picture related to Blood Flow Chart Arteriole Capillary Hydrostatic
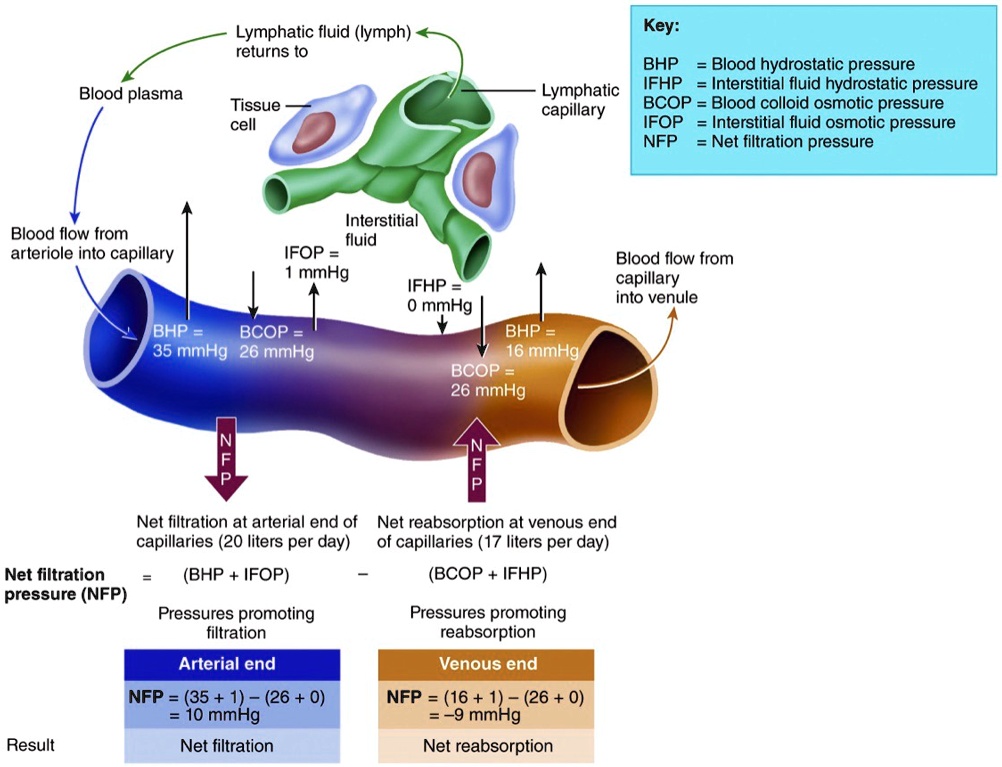
SOLVED Describe The Dynamics Of Capillary Exchange Shown In The Image Lymphatic Fluid lymph
https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/9f5e3b39b51b452087a880199594b7d2.jpg
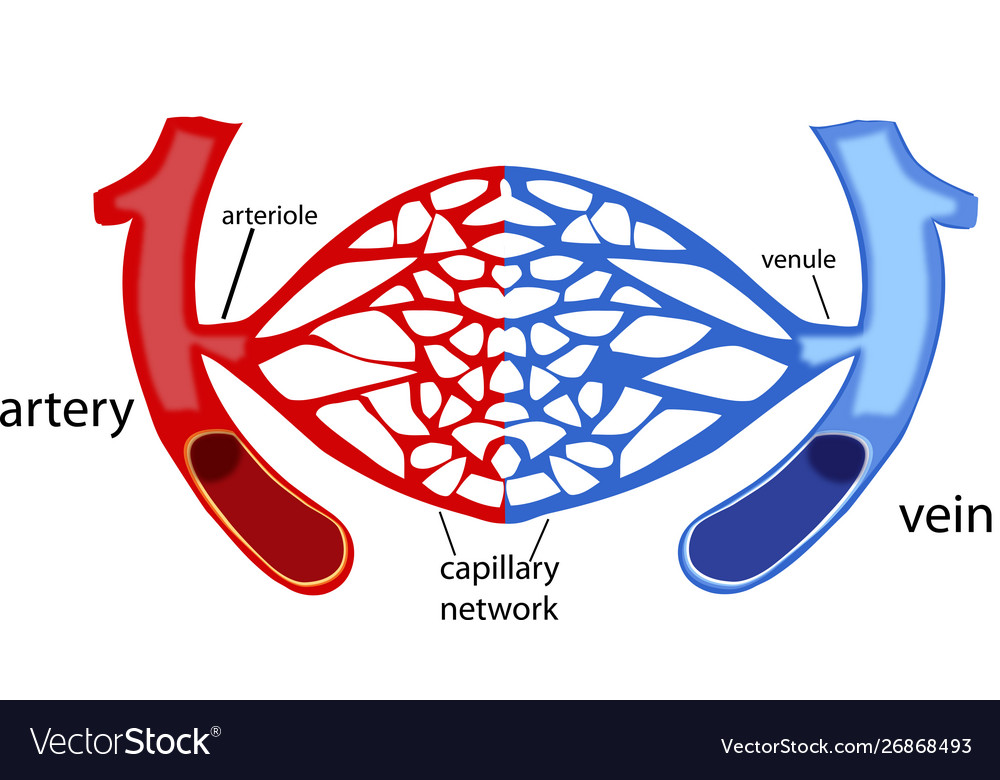
Arteriole Stock Illustrations 379 Arteriole Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
https://thumbs.dreamstime.com/b/blood-vessels-direction-scheme-oxygen-nutrients-flow-heart-waste-flow-to-cells-vector-illustration-educational-190053682.jpg

Theoretical Prediction Of Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure As A Function Download Scientific
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/298797827/figure/fig1/AS:380897254756352@1467824390211/Theoretical-prediction-of-capillary-hydrostatic-pressure-as-a-function-of-ratio-of.png
One form of hydrostatic pressure is blood pressure the force exerted by blood upon the walls of the blood vessels or the chambers of the heart Blood pressure may be measured in capillaries and veins as well as the vessels of the pulmonary circulation however the term blood pressure without any specific descriptors typically refers to Hydrostatic pressure is stronger in the arterial ends of the capillaries while osmotic pressure is stronger at the venous ends of the capillaries Interstitial fluid is removed through the surrounding lymph vessels and eventually ends up rejoining the blood
Blood hydrostatic pressure is the force exerted by the blood confined within blood vessels or heart chambers Even more specifically the pressure exerted by blood against the wall of a capillary is called capillary hydrostatic pressure CHP and is the same as capillary blood pressure Even more specifically the pressure exerted by blood against the wall of a capillary is called capillary hydrostatic pressure CHP and is the same as capillary blood pressure CHP is the force that drives fluid out of capillaries and into the tissues

Capillary Bed Diagram
https://o.quizlet.com/Br0RhfJBYfYnMZX7JR7O-Q_b.png
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CapillaryMicrocirculation-58e6a27d3df78c5162359063.jpg)
Capillary Exchange Diagram
https://www.thoughtco.com/thmb/Z1oW1nSNcSIgXu5XQPP_0FmK1Nk=/1500x1000/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CapillaryMicrocirculation-58e6a27d3df78c5162359063.jpg

https://histology.oit.duke.edu › MBS › Videos › Phys
Arterioles are the dominant site of resistance to blood flow within the organ Capillaries are the site of exchange Balance between hydrostatic and oncotic forces determines the direction of fluid movement either into or out of the capillaries Veins are the low resistance conduits for venous return and volume reservoirs 6

https://pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu › janetwanglee › chapter › blood …
If the sphincters are open the blood will flow into the associated branches of the capillary blood If all of the sphincters are closed then the blood will flow directly from the arteriole to the venule through the thoroughfare channel see Figure 7 17

Hydrostatic Pressure Capillary

Capillary Bed Diagram
/CapillaryBed-58e6a2245f9b58ef7ef79cd2.jpg)
An Illustrated Guide To Capillary Fluid Exchange
Arteriole And Venule Stock Illustration Illustration Of Histology The Best Porn Website

Capillary Fluid Exchange USMLE Strike

Capillary Exchange Diagram

Capillary Exchange Diagram
Capillary Exchange Diagram
Blood Vessels
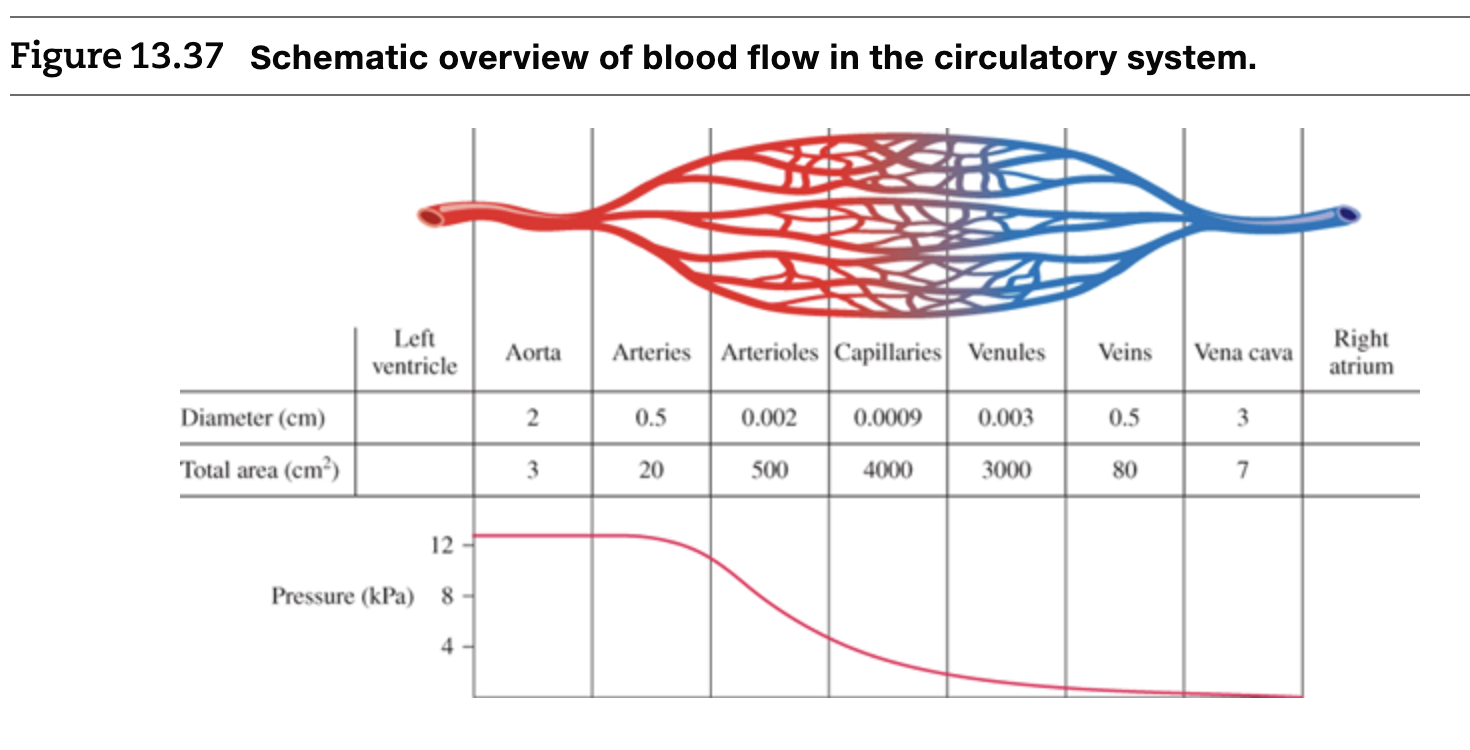
Solved Figure 13 37 Schematic Overview Of Blood Flow In The Chegg
Blood Flow Chart Arteriole Capillary Hydrostatic - Blood hydrostatic pressure is the force exerted by the blood confined within blood vessels or heart chambers Even more specifically the pressure exerted by blood against the wall of a capillary is called capillary hydrostatic pressure CHP and is the same as capillary blood pressure