Bedside Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart Refer to Self Management of diabetes guideline if the patient wishes to self Monitor 2 2 Monitor Blood glucose 2 3 If Blood glucose 11 mmol l follow the guidance flow chart For Adults without a diagnosis of diabetes refer to Diagnosis Guideline Capillary blood glucose 4 mmol l refer to Hypoglycaemia Guideline
Vision of blood glucose testing and monitoring for patients within Hywel Dda U are staying in an emergency unit a clinical decision unit or an in patient ward In this guideline the term in patient area refers unless otherwise stated to emergency units clinical decision units and in patient wards and the term patient refers to a per Evidence based process for blood glucose BG and blood ketone BK monitoring in the inpatient setting There is also a short section providing advice for aged and residential care facilities
Bedside Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart

Bedside Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart
https://image.isu.pub/120717073221-583ac258ffe64e05a79f73164213fc69/jpg/page_1.jpg
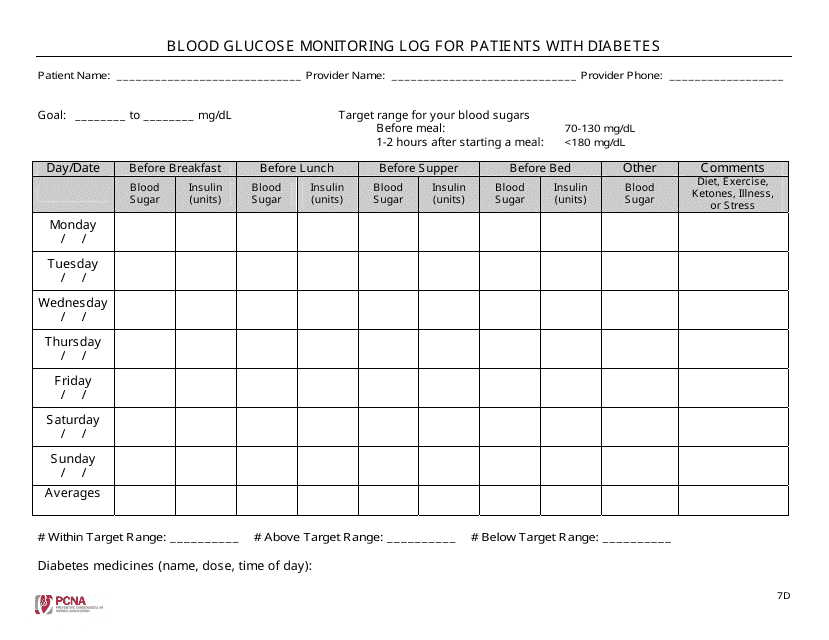
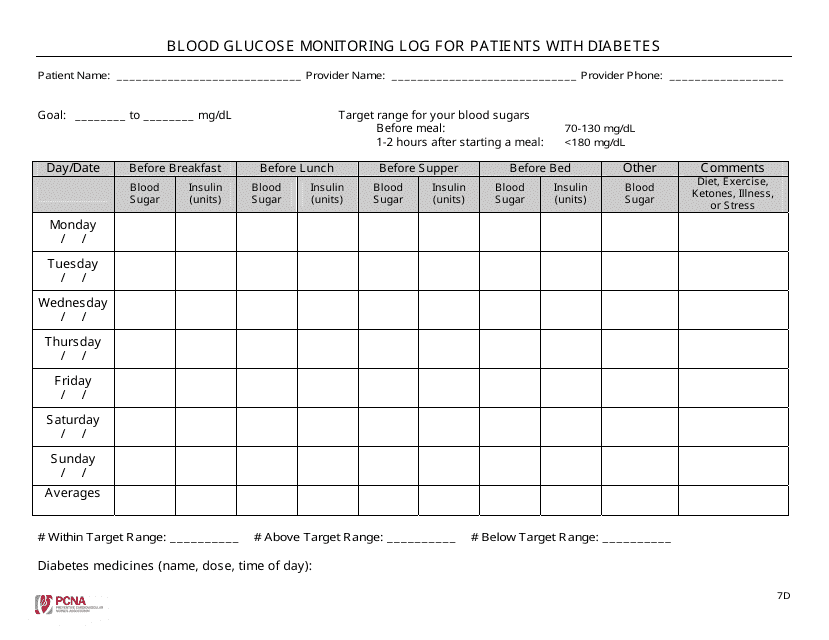
Blood Glucose Monitoring Log For Patients With Diabetes Download Fillable PDF Templateroller
https://data.templateroller.com/pdf_docs_html/2664/26645/2664539/blood-glucose-monitoring-log-for-patients-with-diabetes_big.png
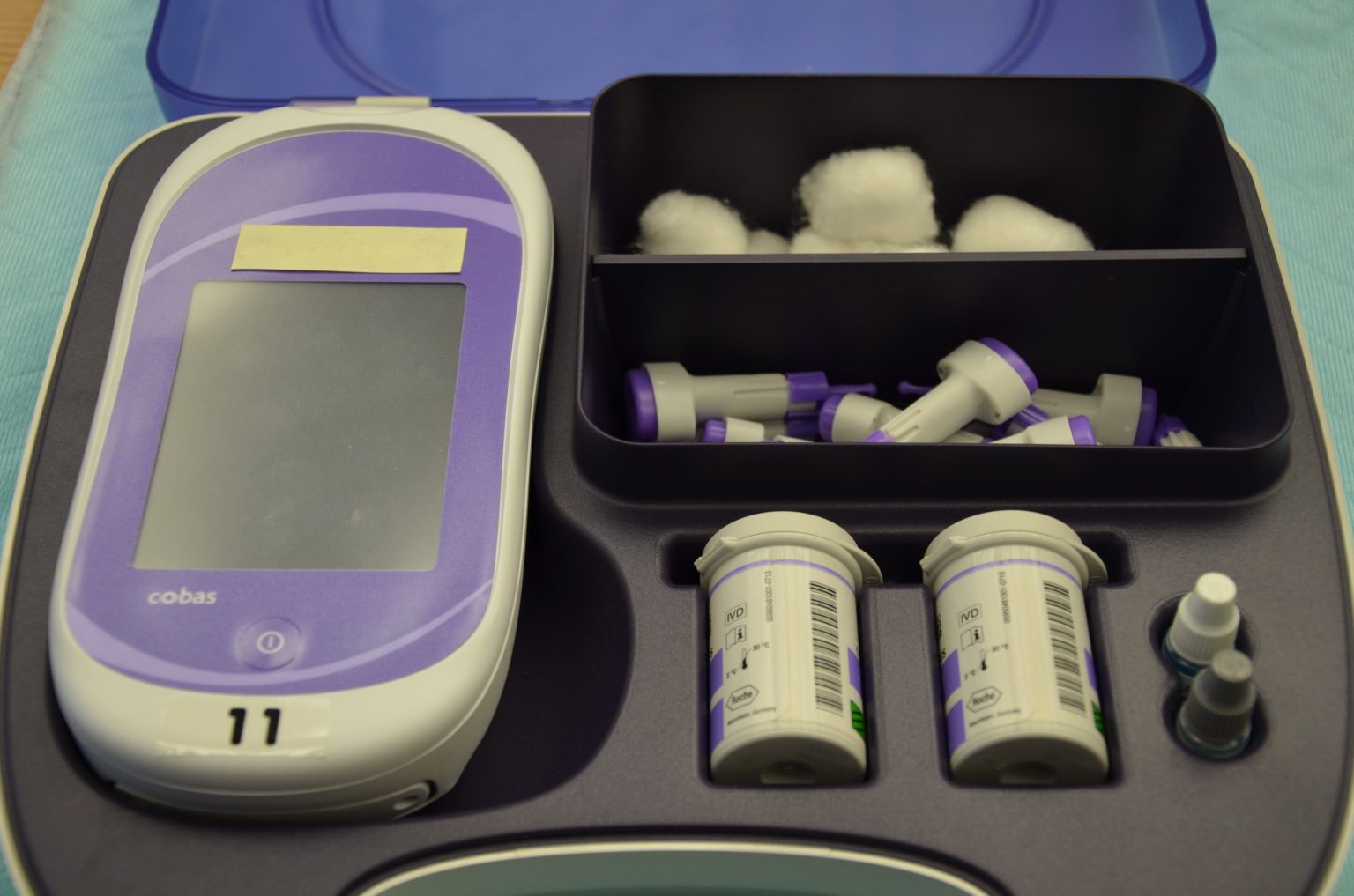
19 2 Blood Glucose Monitoring Nursing Skills 2e
https://wtcs.pressbooks.pub/app/uploads/sites/29/2020/11/DSC_1130-1-2048x1356.jpg
Routine blood glucose monitoring with a bedside point of care POC glucometer is needed for all patients admitted to the hospital with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus e g T1DM T2DM CF related DM etc BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING CHART for patients not on intravenous insulin Normal range 4 0 7 0mmol L Acceptable range whilst in hospital is 4 0 11 0mmol L excluding pregnancy If patient is unwell or has ketones seek advice Initial monitoring should be before meals and before bed Review according to clinical condition
The modern management of hospitalized patients with diabetes includes capillary blood glucose determinations at the bedside This measure is analogous to an additional vital sign for people with diabetes The rapidity with which results can be obtained and therapeutic decisions made can improve management and conceivably Monitor BG at least every two to four hours while the patient is taking nothing by mouth and dose with rapid acting insulin as needed Avoid look alike sound alike insulins Use barcode scanning when dispensing and administering medications Standardize dosing using electronic order sets in the EHR Set maximum dose alerts when possible
More picture related to Bedside Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart
Blood Glucose Level Recording Chart Templates At Allbusinesstemplates
https://www.allbusinesstemplates.com/thumbs/94101eb7-89d4-42d2-aa31-217c60174b7a_1.png

PDF Educational Intervention Together With An On line Quality Control Program Achieve
https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/7563146_Educational_intervention_together_with_an_on-line_quality_control_program_achieve_recommended_analytical_goals_for_bedside_blood_glucose_monitoring_in_a_1200-bed_university_hospital/links/00463528b2eee4b969000000/largepreview.png
![]()
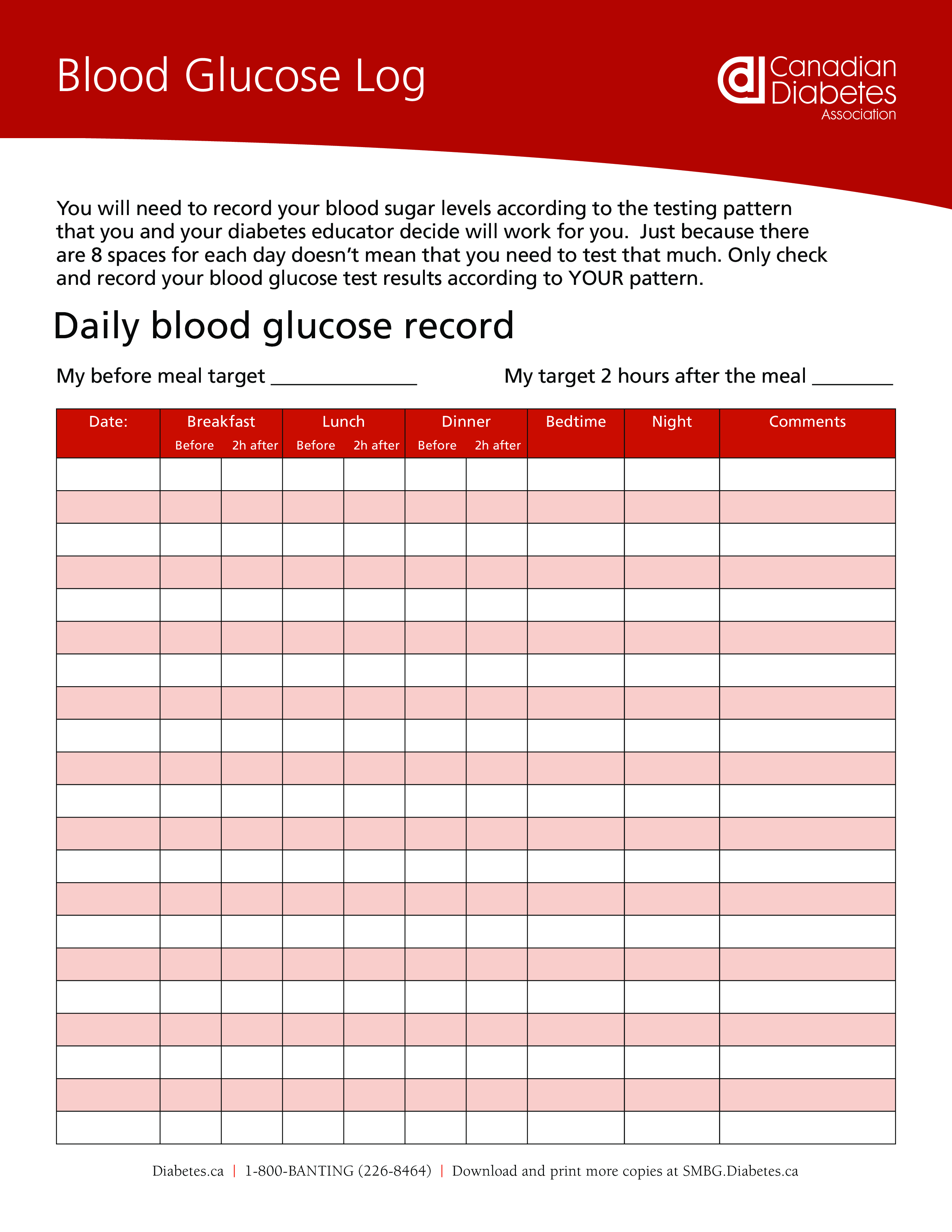
Free Blood Glucose Log Printable Pdf
https://printable-map-az.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/printable-blood-sugar-chart-printable-blood-pressure-log-mine-free-printable-blood-sugar-tracking-chart.png
How is blood glucose monitored There are three ways to measure blood glucose 1 Glycated haemoglobin HbA1c A blood check ordered by your GP or NP one to four times a year The result reflects an average of the level of glucose in your blood for the last 2 to 3 months Note your HbA1c result is not the same as your BGL 2 Blood glucose To get the most out of your blood glucose checks review the data with your diabetes care team during your visits Work with your diabetes care team to use the data you re collecting to make decisions about what you eat how active you are during the day and adjusting your medications
Measure blood glucose level within 2 hours after food intake Pre Meal Blood Glucose Level Measure blood glucose level more than 2 hours after food intake 7 Blood glucose monitoring station documentation Signature and Date The healthcare professional documenting the glucose check should sign and date the record Blood glucose monitoring Explain and offer glucose monitoring and start if users agree or spontaneously request it Encourage monitoring if control is sub optimal i e HbA1c 58 mmol mol 7 5 and especially if insulin is likely to be needed soon this may avoid starting insulin and monitoring

Top 6 Blood Glucose Monitoring Charts Free To Download In PDF Format
https://data.formsbank.com/pdf_docs_html/121/1216/121610/page_1_thumb_big.png
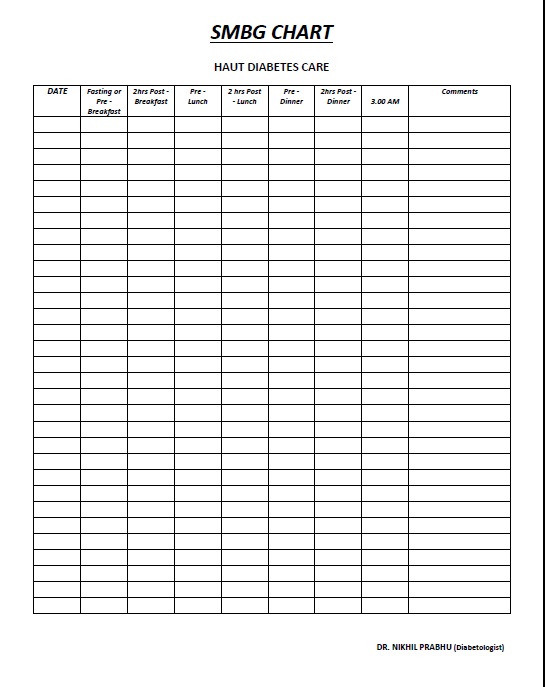
Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Chart Dr Nikhil Prabhu s Blog Diabetes Care
http://blog.drnikhilprabhu.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/SMBG.jpg

https://doclibrary-rcht.cornwall.nhs.uk › DocumentsLibrary …
Refer to Self Management of diabetes guideline if the patient wishes to self Monitor 2 2 Monitor Blood glucose 2 3 If Blood glucose 11 mmol l follow the guidance flow chart For Adults without a diagnosis of diabetes refer to Diagnosis Guideline Capillary blood glucose 4 mmol l refer to Hypoglycaemia Guideline
https://hduhb.nhs.wales › ...
Vision of blood glucose testing and monitoring for patients within Hywel Dda U are staying in an emergency unit a clinical decision unit or an in patient ward In this guideline the term in patient area refers unless otherwise stated to emergency units clinical decision units and in patient wards and the term patient refers to a per

Continuous Glucose Monitoring Comparison Chart Published The Diabetes Times

Top 6 Blood Glucose Monitoring Charts Free To Download In PDF Format
19 2 Blood Glucose Monitoring Nursing Skills 2e

Blood Glucose Measurement Chart

Glucose Chart Printable
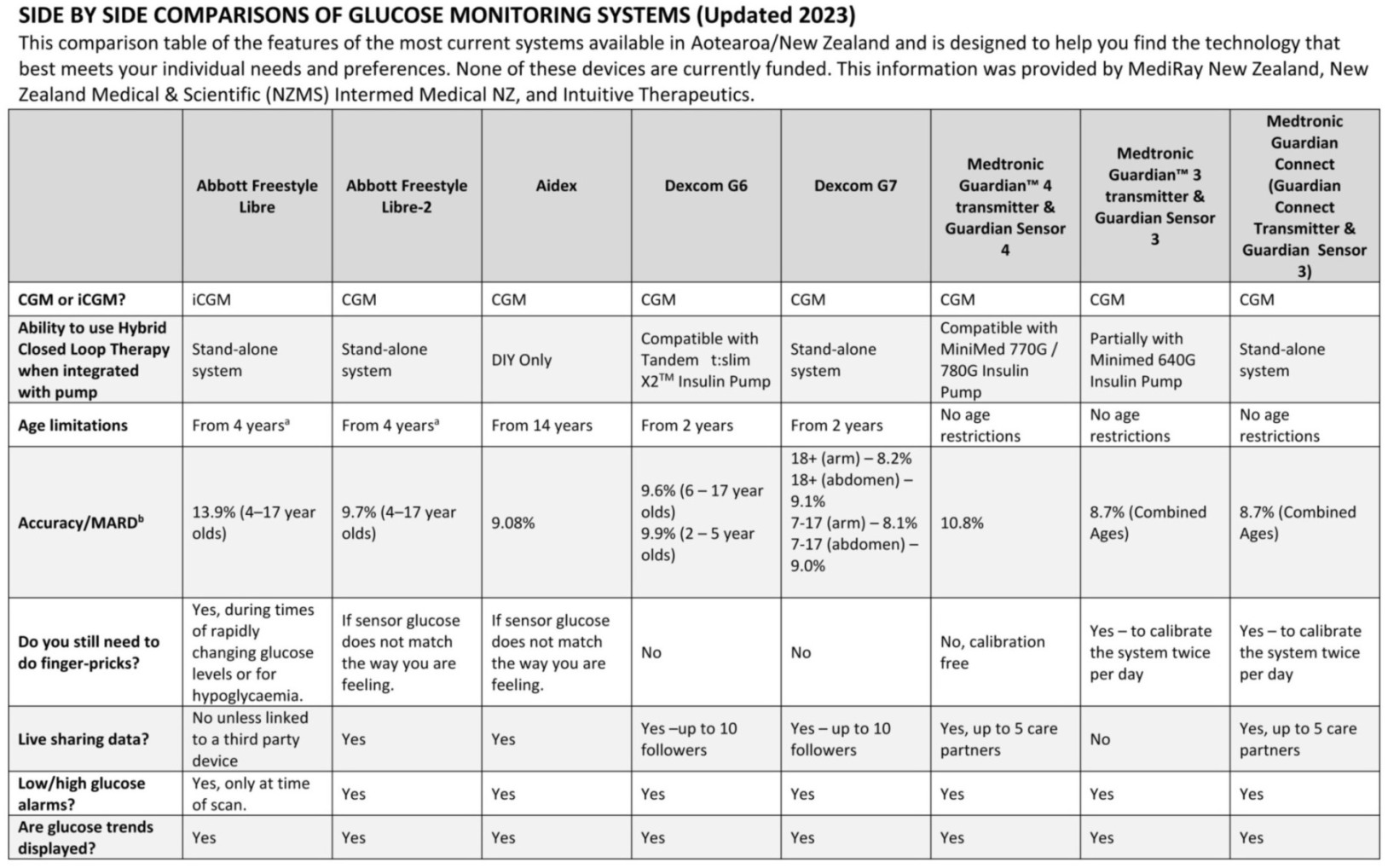
Starship Glucose Monitoring Systems

Starship Glucose Monitoring Systems

Free Printable Blood Glucose Log Sheet Printable Templates Sexiezpix Web Porn

Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart In PDF Download Template

Blood Glucose Chart 6 Free Templates In PDF Word Excel Download
Bedside Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart - One You can monitor blood glucose levels by using a chart that shows blood sugar levels by age The goals for blood sugar glucose in older adults are typically different from those in younger adults Together with your healthcare professional you can establish a tailored management plan by estimating the normal blood glucose levels for your