Atls Blood Loss Chart Blood loss 2000 mL or 40 blood volume Heart rate 140 min Blood pressure decreased Pulse pressure mmHg decreased Respiratory rate 35 min Urine output negligible CNS confused lethargic Unfortunately the classic stages of hemorrhagic shock a la ATLS are of limited clinical relevance in the real world because of
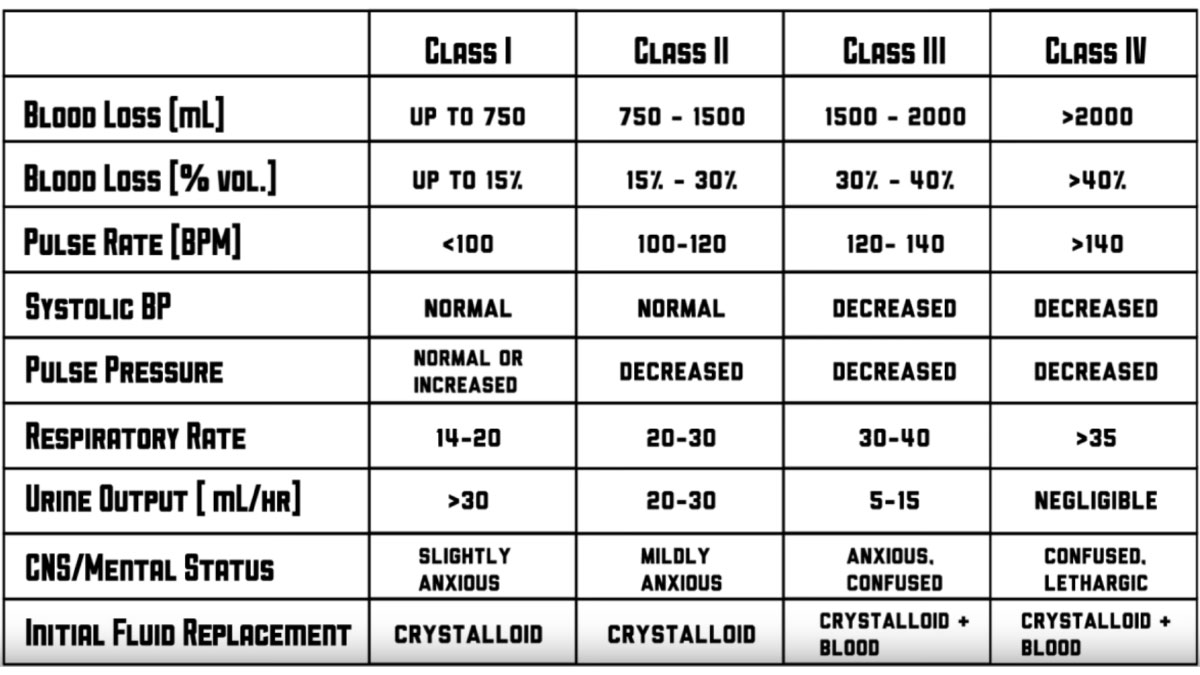
Appropriate management of the massively bleeding trauma patient includes the early identification of bleeding sources followed by prompt measures to minimise blood loss restore tissue perfusion and achieve haemodynamic stability Based on the initial vital signs we estimate the amount of blood loss as Class I up to 15 of blood volume lost Class II 15 30 blood loss Class III 30 40 blood loss Class IV more than 40 of blood loss
Atls Blood Loss Chart

Atls Blood Loss Chart
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/de/9d/9a/de9d9a2b726bdfa698d21be9dfff6de5.jpg
Is Advanced Trauma Life Support ATLS Wrong About Palpable Blood Pressure Estimates REBEL EM
https://rebelem.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/ATLS-1024x576.png
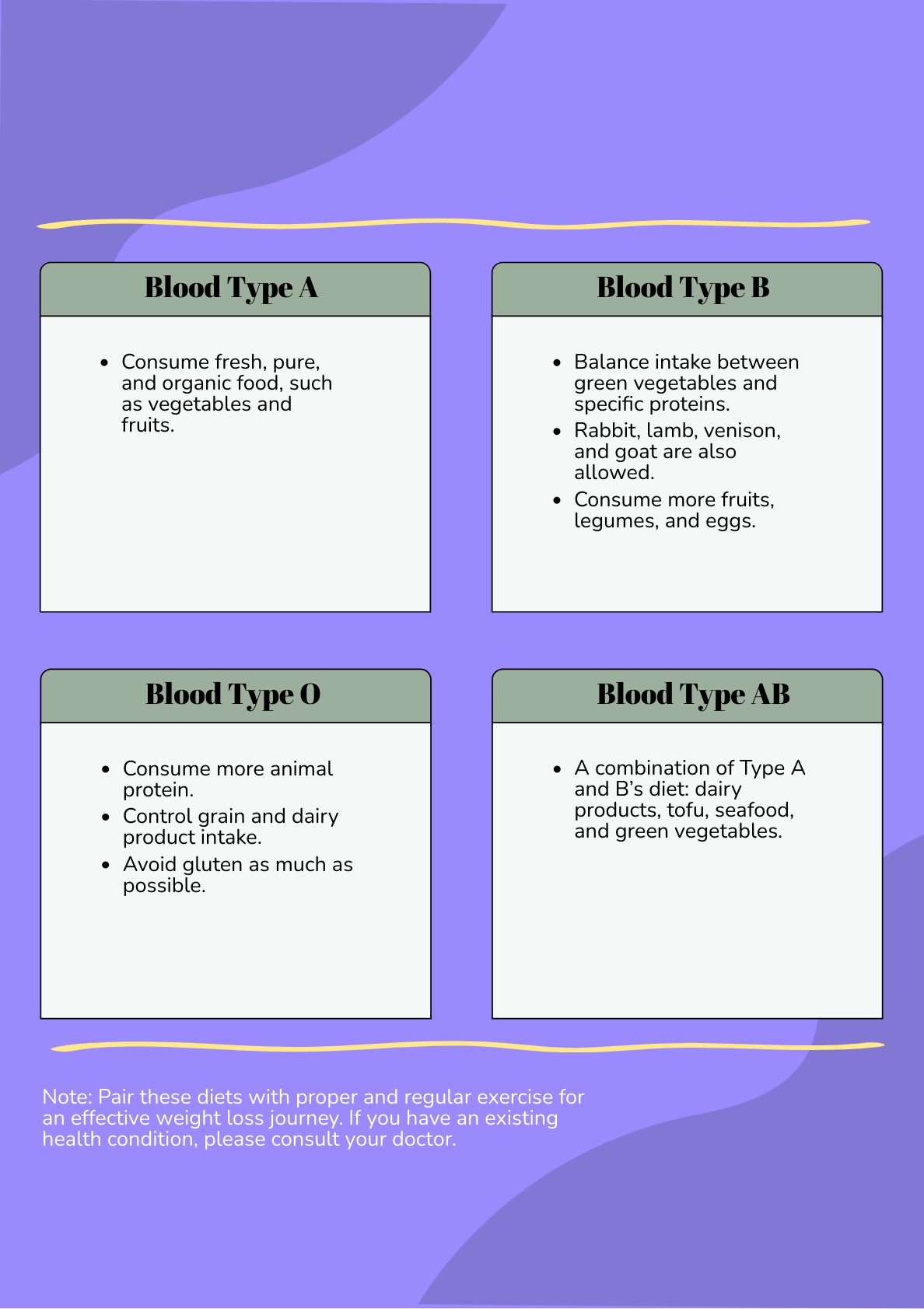
Weight Loss Blood Type Diet Chart In Illustrator PDF Download Template
https://images.template.net/115795/weight-loss-blood-type-diet-chart-yozxc.jpeg
What class of hemorrhage or what of blood volume loss is the first to demonstrate systolic hypotension This is important because prehospital providers and those in the ED typically rely on systolic blood pressure to figure out if their patient is in trouble The answer is Class III or 30 40 But how do you remember the damn percentages Download Table Hemorrhage Classification per ATLS 9th edition Estimated blood loss a based on patient s initial presentation from publication Trauma and Massive Blood Transfusions
Assess pulses before and after reduction and splinting If pulse is lost release and reapply traction splint Ankle brachial index As measured by Doppler systolic blood pressure at ankle divided by systolic blood pressure in right arm left arm is Traditional ATLS teaching held that If only the carotid pulse is palpable the systolic blood pressure SBP is 60 70 mmHg If the carotid and femoral pulses are palpable the SBP is 70 80 mmHg If the radial pulse is also palpable the SBP is 80 mmHg
More picture related to Atls Blood Loss Chart

ATLS Classification Of Blood Loss Based On Initial Patient Presentation Download Table
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Edmund-Am-Neugebauer/publication/236250473/figure/fig2/AS:393322234433548@1470786736954/Flow-chart-of-treatment-modalities-for-the-bleeding-trauma-patient-discussed-in-this_Q640.jpg

ATLS Classification Of Blood Loss Based On Initial Patient Presentation Download Table
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Edmund_AM_Neugebauer/publication/236250473/figure/tbl1/AS:393322238627841@1470786737386/Grading-of-recommendations-after-24-reprinted-with-permission_Q640.jpg
ATLS Pretest PDF Blood Pressure Major Trauma
https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/440017052/original/3357f2919f/1662229350?v=1
The Revised Trauma Score RTS is made up of a combination of results from three categories All of these results can be quickly assessed with minimal equipment a flashlight a watch and a sphygmomanometer since systolic pressure can be obtained through arterial palpation The score range is 0 12 In START triage a patient with an RTS score of For each patient the blood loss was estimated and patients were divided into four groups based on the estimated blood loss corresponding to the ATLS classes of shock The median and interquartile ranges IQR of the heart rate HR systolic blood pressure SBP respiratory rate RR and Glasgow Coma Score GCS were calculated for each group
For each patient the blood loss was estimated and patients were divided into four groups based on the estimated blood loss corresponding to the ATLS classes of shock The median and interquartile ranges IQR of the heart rate HR systolic blood pressure SBP respiratory rate RR and Glasgow Coma Score GCS were calculated for each group Hypovolaemic shock ATLS1 suggests four shock classes based upon vital signs and an estimated blood loss in percent Although this classification has been widely implemented over the past decades there is still no clear prospective evidence to fully support this classification
Atls Classification Of Hemorrhagic Shock
https://medzcool-static.s3.amazonaws.com/media/media/Hemorrhagic-Shock-Classification_dl2doSO.jpg

PDF Vital Signs And Estimated Blood Loss In Patients With Major Trauma Testing The Validity
https://0.academia-photos.com/attachment_thumbnails/40203443/mini_magick20190221-23162-1eehe5j.png?1550794777

https://litfl.com › major
Blood loss 2000 mL or 40 blood volume Heart rate 140 min Blood pressure decreased Pulse pressure mmHg decreased Respiratory rate 35 min Urine output negligible CNS confused lethargic Unfortunately the classic stages of hemorrhagic shock a la ATLS are of limited clinical relevance in the real world because of
https://ccforum.biomedcentral.com › articles
Appropriate management of the massively bleeding trauma patient includes the early identification of bleeding sources followed by prompt measures to minimise blood loss restore tissue perfusion and achieve haemodynamic stability
PPT Overview Of ATLS PowerPoint Presentation Free Download ID 1718931

Atls Classification Of Hemorrhagic Shock
ATLS Blood Pressure Estimation Debate

ATLS Novit 2018 GT Intensive Acute Trauma Care Group

ATLS Novit 2018 GT Intensive Acute Trauma Care Group

ATLS Classification Of Hemorrhagic Shock Simplified

ATLS Classification Of Hemorrhagic Shock Simplified

Calculation Of Total Blood Volume And Estimated Blood Loss Download Scientific Diagram
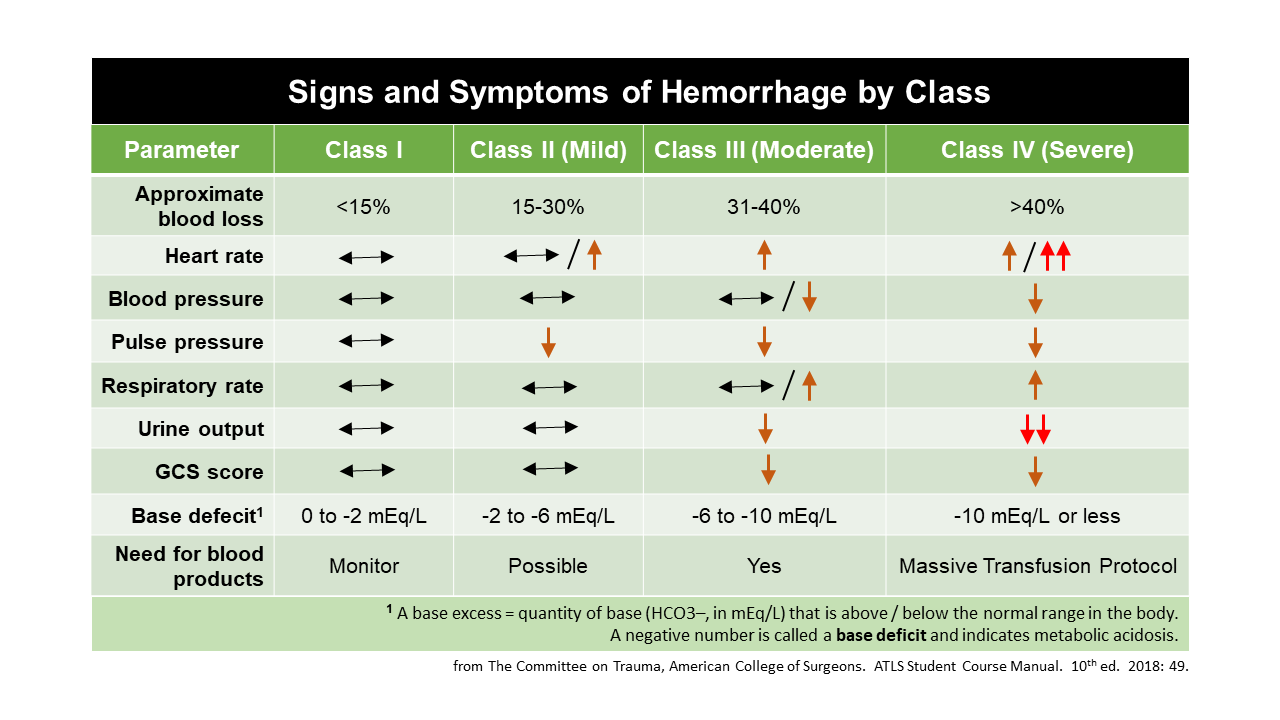
Medical Professionals TOTAL EM
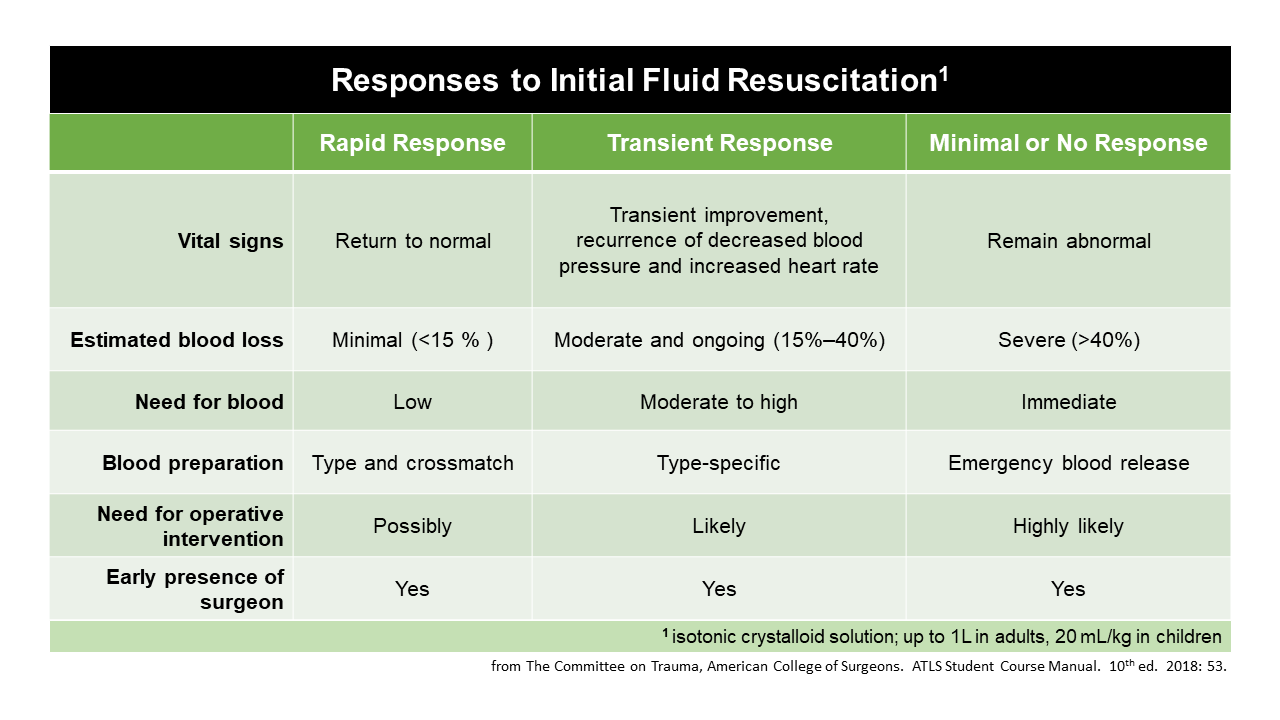
Medical Professionals TOTAL EM
Atls Blood Loss Chart - Assess pulses before and after reduction and splinting If pulse is lost release and reapply traction splint Ankle brachial index As measured by Doppler systolic blood pressure at ankle divided by systolic blood pressure in right arm left arm is
